Introduction
The Agent Cluster is designed to provide horizontal scalability and fail-over capabilities for Agents in HA environments, see JS7 - Agent Cluster. It works without a single point of failure.
Use of a JS7 - Agent Cluster is subject to the JS7 - License.
We find separate tiers in the architecture of Agent Clusters, see JS7 - System Architecture:
- Controller (Cluster) → Director Agent (Cluster)
- Director Agent (Cluster) → Subagent Cluster
We find separate layers for operation and use of Agent Clusters:
- Operational Layer: Subagents and Director Agent Instances
- Subagents and Director Agent instances are similarly installed.
- Director Agent instances orchestrate Subagents. They include a Subagent that can be used if users wish to execute jobs from a Director Agent.
- Functional Layer: Subagent Cluster and Director Agent Cluster
- Jobs are assigned Subagent Clusters to specify that the jobs can be executed by any Subagent that is a member of the Subagent Cluster. The Subagent Cluster rules if a different Subagent will be chosen in case of fail-over only (fixed-priority scheduling, active-passive cluster) or for each next execution of a job (round-robin, active-active cluster).
- The Director Agent Cluster is independent from Subagent Clusters. The purpose of clustering is to provide high availability for the role of orchestrating Subagents.
Consider the wording in this article:
- Fail-over is an automated operation that occurs when a Subagent is aborted or killed. Fail-over is applied in case of abnormal termination.
- Switch-over is a manual operation performed by users disabling/enabling Subagents.
This article is focused on fail-over of Subagents. For fail-over scenarios with Director Agent Clusters see JS7 - How to fail-over and switch-over between Director Agent instances
For command line references see the JS7 - Agent - Command Line Operation article.
Fail-over Operation
Fail-over occurs when an Active Subagent is terminated abnormally. Fail-over includes that the task currently being executed by the Subagent is considered to have failed and that the related order is set to a failed state. An Inactive Subagent is no longer considered for execution of jobs by a Director Agent:
- Subagent Clusters configured for round-robin scheduling will execute jobs with the remaining Subagents.
- Subagent Clusters configured for fixed-priority scheduling will switch execution of jobs to the next Subagent.
Fail-over can be caused by the following actions:
- The Active Subagent is killed, for example:
- for Unix with a SIGKILL signal corresponding to the command:
kill -9 - for Windows with the command:
taskkill /F
- for Unix with a SIGKILL signal corresponding to the command:
- From the command line the Agent's Instance Start Script can be used like this:
agent_<port>.sh | .cmd abortagent_<port>.sh | .cmd kill
Fail-over will not occur when:
- the Active Subagent is stopped normally from the command line:
agent_<port>.sh | .cmd stop
- the operating system is shut down and
systemd/init.dor a Windows Service are in place to stop the Subagent normally.
Fail-over happens within a short period of time, typically in 2-3s.
Round-robin Subagent Cluster
Scenario for normal Cluster Operation
The JS7 - How to set up an Agent Cluster article explains how to set up a number of Subagents.
- Create a workflow from the Configuration view and assign the same Agent Cluster to all jobs. Once the configuration is completed deploy the workflow.
- The Agent Cluster is configured for round-robin scheduling and executes each subsequent job with the next Subagent.
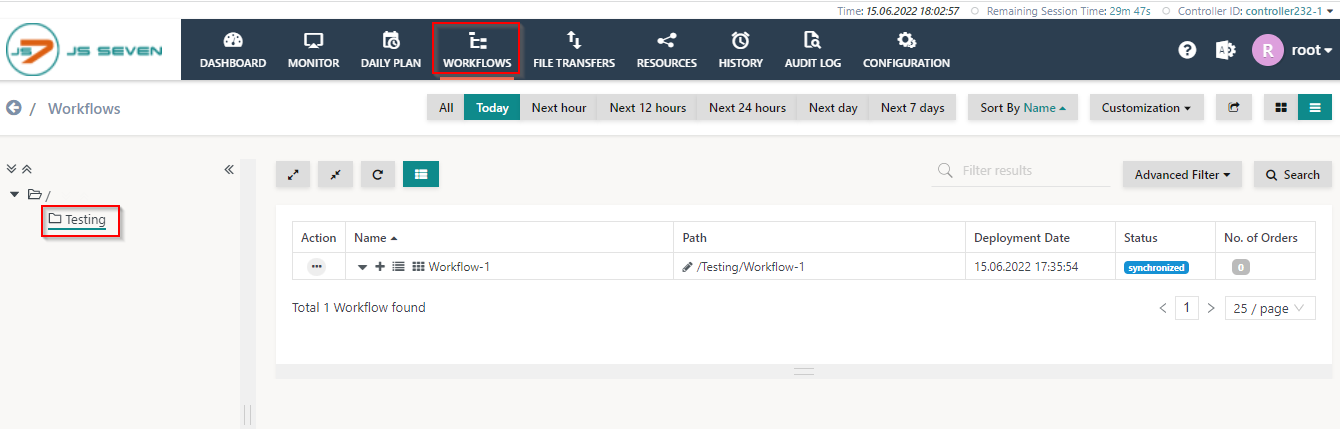
- To test cluster behavior navigate to the Workflows view and select a workflow from the tree.
- Expand the workflow and add an order.
- Once the workflow has completed successfully open the log from the history panel.
- In the log, you can identify that all jobs use different Subagents as the Agent Cluster is set up for round-robin scheduling. Each next job is executed with the next Subagent.
Scenario for fail-over Cluster Operation
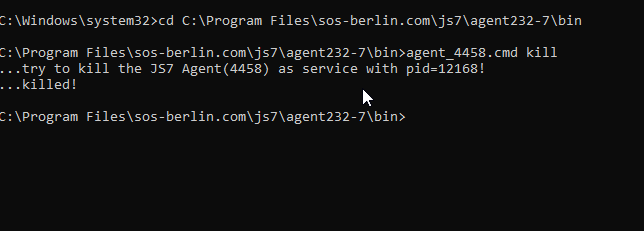
- Kill one of the Active Subagents from the command line to force fail-over with one of the below commands.
- An Active Subagent is killed, for example:
- on Unix with a SIGKILL signal corresponding to the command:
kill -9 - on Windows with the command:
taskkill /F
- on Unix with a SIGKILL signal corresponding to the command:
- From the command line, the Agent Instance Start Script can be used like this:
agent_<port>.sh | .cmd abortagent_<porr>.sh | .cmd kill
- An Active Subagent is killed, for example:
- Check the order log to verify that jobs in the workflow are successfully executed with all the remaining Subagents.
Fixed-priority Subagent Cluster
Scenario for normal Cluster Operation
This scenario is similar to the Scenario for normal Cluster Operation of a round-robin Subagent Cluster with the exception that jobs are assigned a Subagent Cluster which is set up for fixed-priority scheduling.
Fixed-priority means that all jobs will be executed with the first Subagent unless it becomes unavailable and only then jobs will be executed with the next Subagent.
Scenario for fail-over Cluster Operation
- Kill the Active Subagent from the command line to force fail-over with one of the commands listed below.
- The Active Subagent is killed, for example:
- on Unix with a SIGKILL signal corresponding to the command:
kill -9 - on Windows with the command:
taskkill /F
- on Unix with a SIGKILL signal corresponding to the command:
- From the command line the Agent Instance Start Script can be used like this:
agent_<port>.sh | .cmd abortagent_<porr>.sh | .cmd kill
- The Active Subagent is killed, for example:
- Check the order log to verify that any jobs in the workflow are successfully executed with the next Subagent.
Further Resources
- JS7 - Agent Cluster
- JS7 - How to set up an Agent Cluster
- JS7 - Management of Agent Clusters
- JS7 - How to fail-over and switch-over between Director Agent instances