Introduction
- The Fork Instruction is offered to fork and to join orders to enable parallel processing in a workflow.
- The Fork Instruction allows to create a number of parallel branches that process any further instructions and jobs.
- Branches can include any number of instructions and jobs.
- The max. number of parallel branches is limited to 15.
- When an order enters a Fork Instruction then a child order is created for each branch. Each child order will pass the nodes in its branch independently of parallel child orders.
- While child orders are running, the parent order waits for its child orders to be completed, i.e. to arrive at the Join Instruction. The parent order therefore is assigned the WAITING state, see JS7 - Order State Transitions.
- The following options apply to error handling with child orders:
- Default: If a job in a child order's branch fails then the child order is assigned the FAILED state. Such child orders require user intervention to resume execution. When resuming a child order then it can restart from the same or from any previous or later node in the child order's branch. This includes the option to move a child order to the branch end.
- Note that resuming a child order from its branch end will not modify its FAILED state that is adopted by the parent order.
- Users who want to force successful execution of a failed child order should resume the child order from a job node that is executed successfully.
- If a job in a child order's branch fails then the child order terminates immediately and the parent order is put to the FAILED state. This behavior can be activated by use of the Join if Failed flag of the Fork Instruction.
- Default: If a job in a child order's branch fails then the child order is assigned the FAILED state. Such child orders require user intervention to resume execution. When resuming a child order then it can restart from the same or from any previous or later node in the child order's branch. This includes the option to move a child order to the branch end.
- Child orders cannot be cancelled as they are required to pass the Join Instruction. Should child orders not be intended to pass the remaining instructions in a branch then a user can resume failed child orders from the Join Instruction.
- Consider that child orders can take the role of parent orders in nested Fork Instructions.
- The following options apply to error handling with child orders:
Feature Video
This video explains how to create parallel jobs in a workflow that can be nested and joined.
Workflow Instruction: Fork/Join
Simple Fork/Join
Download Workflow Example: pdwFork.json
Explanation:
- The Fork Instruction is used for two parallel branches, the names of the branches can be specified.
- After the child orders for both branches have arrived with the Join Instruction then the parent order will continue with the next node.
- The Join If Failed property determines the behavior in case of failed child orders:
- If checked then failed child orders terminate immediately and cause the parent order to adopt the FAILED state.
- If not checked then failed child orders will be halted and allow user intervention to resume execution from an node of the child order's branch.
Nested Fork/Join
Download Workflow Example: pwdForkNested.json
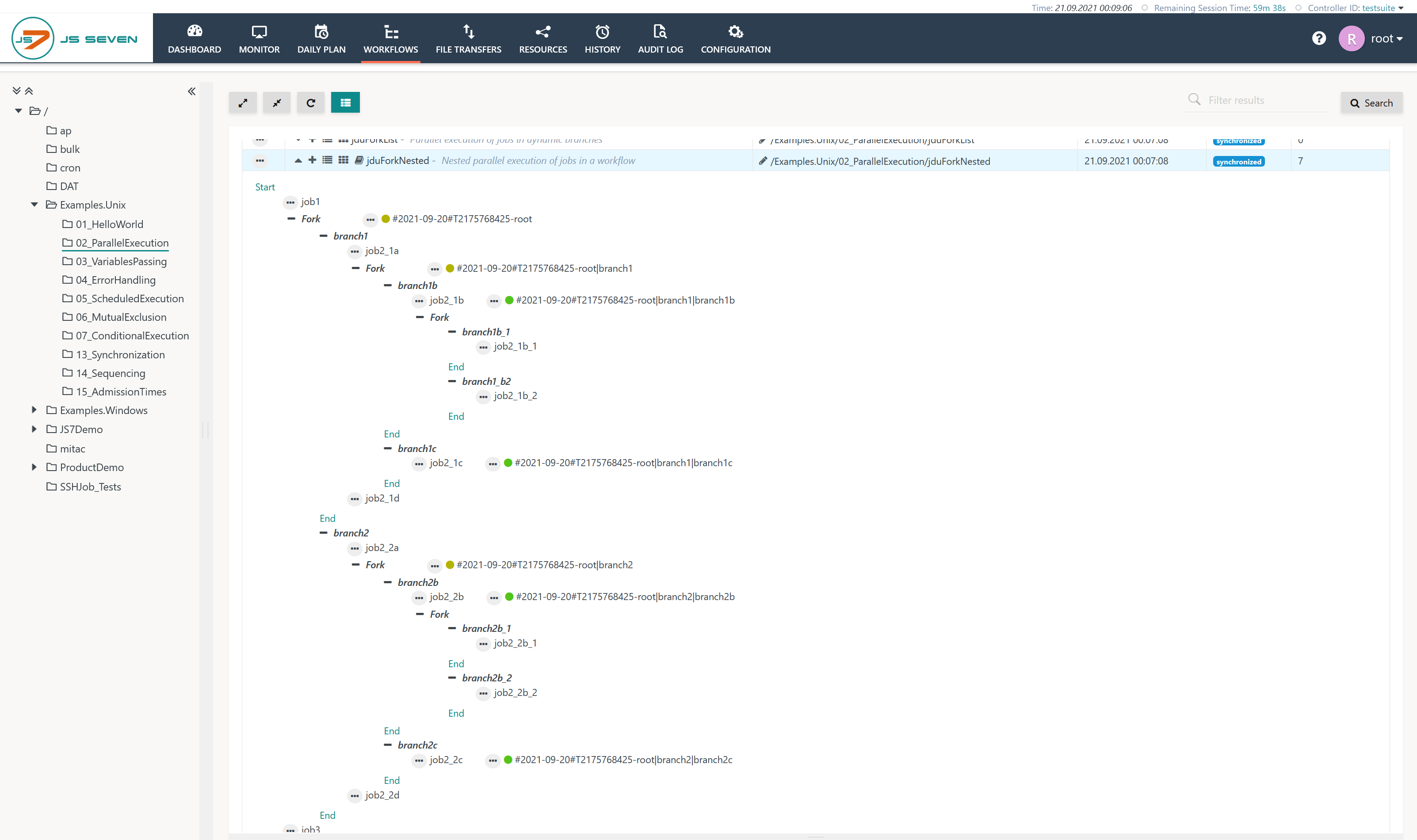
The Workflows View for the above workflow will display parallel child orders like this:
Explanation:
- The Workflows View shows three levels of orders: the parent order sitting with the initial Fork Instruction and two levels of child orders passing their respective branches.
- As soon as the inner child orders are completed then the outer level of parent orders continues and completes respectively.
Overview
Content Tools