Introduction
- Environment variables are a means to parameterize jobs.
- Environment variables allow read and write operations, however, modifying the value of an environment variable works within the scope of the current job only.
- Environment Variables are used with uppercase letters only. For Windows environments the uppercase/lowercase spelling makes no difference, however, for Unix different spellings create different environment variables.
- A number of environment variables are available to shell jobs by default.
- Additional environment variables can be added per job configuration from JS7 - Order Variables, from node arguments and from JS7 - Job Resources.
Environment Variables that are automatically available to Shell Jobs
The following environment variables are available to all shell jobs. They are provided from the Agent Instance Script and from the Agent binary files.
Depending on the OS, environment variables are syntactically used like this:
- Windows:
%JS_AGENT_HOME% - Unix:
$JS_AGENT_HOMEor${JS_AGENT_HOME}
| Category | Environment Variable | Description | Adjustable by Script | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agent | JS7_AGENT_PORT | The number of the port that an Agent is listening to for messages sent from a Controller. | Agent Instance Script | 4445 |
JS7_AGENT_HTTP_PORT | Same as JS7_AGENT_PORT except that a network interface can be specified, e.g. localhost:4445 to limit access to the given network interface. This environment variable will not be available if the Agent is configured not to listen to an HTTP port. | Agent Instance Script | 4445 | |
JS7_AGENT_HTTPS_PORT | The SSL port used in addition to the HTTP port. A network interface can be specified, e.g. myhost:4447 to limit access to the given network interface. This environment variable will not be available if the Agent is not configured to listen to an HTTPS port. | Agent Instance Script | n/a | |
JS7_AGENT_USER | The account that the Agent is operated for. For Unix OS the account can be specified from the Agent Instance Script. For Windows OS the service account assigned to the Agent with the Windows Service Panel is provided. | Unix: Agent Instance Script Windows: Service Account | n/a | |
| The Agent's home directory, i.e. the directory in which the Agent has been installed. For Windows OS this could be e.g. For Unix OS environments this could be e.g. | Agent Instance Script | n/a | |
JS7_AGENT_DATA | The Agent's data directory with sub-directories for temporary data, configuration data etc. The name of the data directory is created from the prefix For Windows OS this could be e.g. For Unix OS environments this could be e.g. The Agent's home directory | Agent Instance Script | JS7_AGENT_HOME/var_<JS7_AGENT_HTTP_PORT> | |
JS7_AGENT_CONFIG_DIR | The Agent's configuration directory. | Agent Instance Script | JS7_AGENT_DATA/config | |
JS7_AGENT_LOGS | The Agent's directory for log files. | Agent Instance Script | JS7_AGENT_DATA/logs | |
JS7_AGENT_PID_FILE | The Agent's creates the agent.pid file in the logs directory that contains the process ID of the current Agent being run. | Agent Instance Script | JS7_AGENT_DATA/logs/agent.pid | |
JS7_AGENT_WORK_DIR | The Agent's working directory. | Agent Instance Script | JS7_AGENT_DATA | |
JS7_AGENT_TZ | The time zone of the Agents' computer | Agent Start Script | Etc/UTC | |
| Run-time | JS7_RETURN_VALUES | The location of a temporary file created by the Agent for the current shell job. This can be used to append pairs of names and values with each pair being added on a separate line. After execution of the shell job the Agent will add order variables with the respective names and values found from this file. | n/a | |
JAVA_HOME | The location of the Java installation directory as used by the Agent. | Agent Instance Script | JAVA_HOME | |
JAVA_OPTIONS | Java options for the Agent loading its JVM are different from Java options used for jobs that run individual Java programs. Therefore the Agent Start Script allows the JS7_AGENT_JOB_JAVA_OPTIONS environment variable to be set, e.g. to limit a job's memory consumption with the option -Xmx32m. Therefore this environment variable is populated from the Java job options environment variable. | Agent Instance Script | JS7_AGENT_JOB_JAVA_OPTIONS | |
| File Transfer | JS7_YADE_HOME | The home directory of the YADE installation. By default the Agent ships with YADE included in the yade sub-directory of the Agent's home directory. | n/a | JS7_AGENT_HOME/yade |
JS7_YADE_BIN | The path to the YADE start script. Usually this is located in the bin sub-directory of the directory specified by JS7_YADE_HOME. | n/a | Unix: Windows: | |
JS7_YADE_DMZ_BIN | The location of the start script used to run YADE in a DMZ. By default the directory is the same as JS7_YADE_HOME/bin and the file name is yade4dmz.sh. | n/a | Unix: Windows: | |
JS7_YADE_CONFIG_DIR | The location of the configuration directory that holds YADE file transfer configuration files (*.xml, *.ini). By default the Agent's configuration directory is used. | Agent Instance Script | JS7_AGENT_CONFIG_DIR |
Environment Variables from Job Resources for Shell Jobs
The environment variables listed in this section are not available by default.
- They are provided from default Job Resources that are available for download and that can be assigned to any workflows and jobs.
- Fnd the archive
Defaults.zipfor download here: JS7 - Download. - The .zip archive includes the following Job Resources:
Default.jobresource.jsoneMailDefault.jobresource.json
- After import the Job Resources are available in the JOC Cockpit Configuration view, in the
/Defaultsfolder and with the namesDefaultandeMailDefault.
- Fnd the archive
- They can be provided from individual JS7 - Job Resources.
Users are free to define their own job resources to publish individual environment variables to workflows and jobs.
Job Resource: Default
Find explanations from the JS7 - Default Job Resource article.
Job Resource: eMailDefault
Find explanations from the JS7 - eMailDefault Job Resource article.
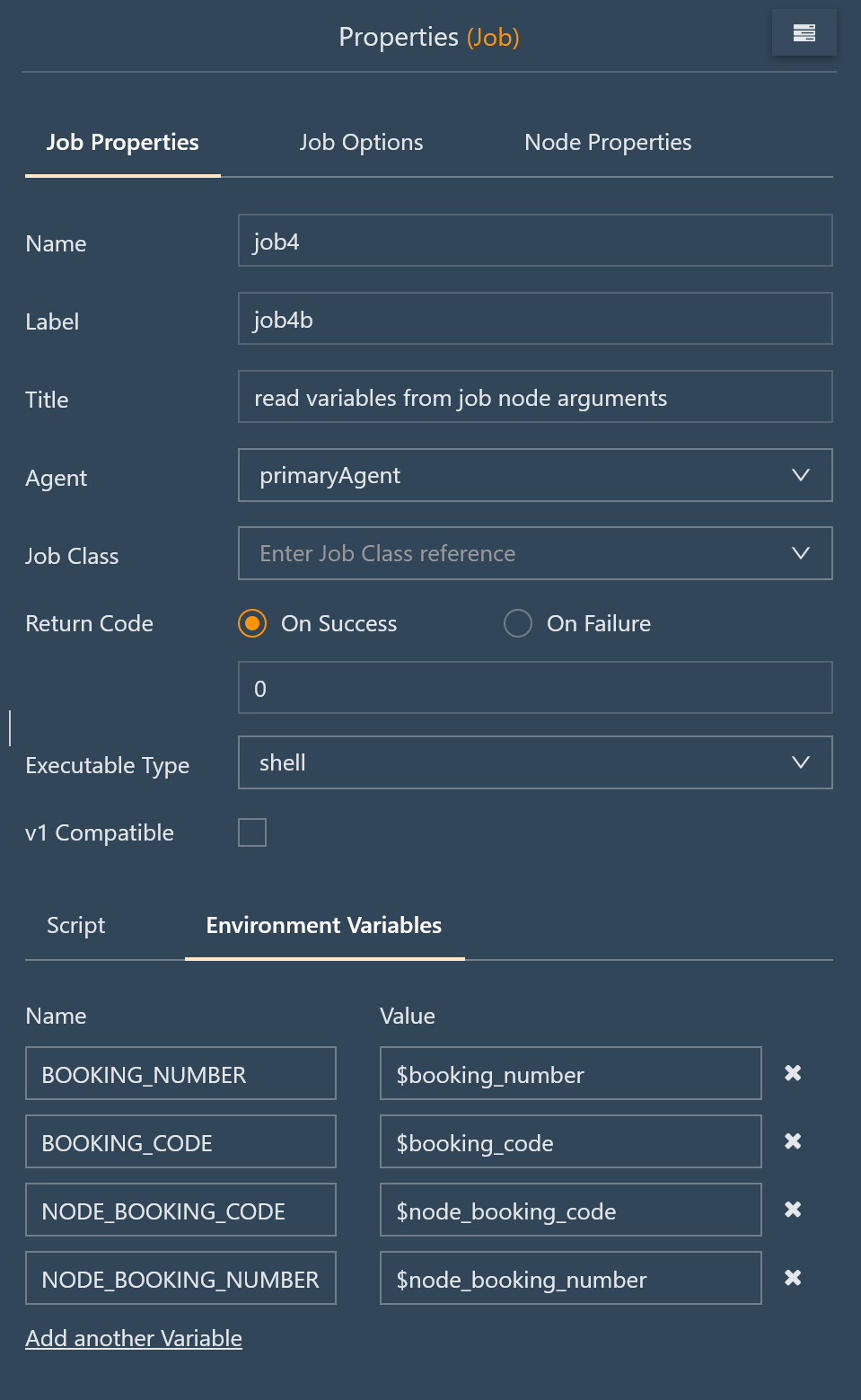
Environment Variables from Job Properties
- Job properties allow environment variables that are forwarded to the job script to be specified.
- The values of environment variables can be specified from:
- constant string values
- order variables
- node arguments
- For details see
Explanation:
- Users are free to choose the names of environment variables compliant to their OS. Such names are automatically converted to uppercase letters.
- Environment variables can be assigned values from order variables and from node arguments. Such variables are preceded by a
$and follow the spelling of the relevant variable or argument. - Caveat: Any existing environment variables with the same name will be overwritten from the job configuration. You can e.g. specify a
PATHenvironment variable if the intention is to modify this OS environment variable for use with a specific job.