The agent architecture has some prerequisites.
Make sure that Main JobScheduler can communicate with the Agent JobScheduler and vice versa.
For this, edit the ./config/scheduler.xml of the Main JobScheduler:
...
<security ignore_unknown_hosts="yes">
...
<allowed_host host="[host or IP of the Agent JobScheduler]" level="all"/>
</security>
...
and edit the ./config/scheduler.xml of the Agent JobScheduler:
...
<security ignore_unknown_hosts="yes">
...
<allowed_host host="[host or IP of the Main JobScheduler]" level="all"/>
</security>
...
Make sure that no firewall restricts the communication.
See also http://www.sos-berlin.com/doc/en/scheduler.doc/remote_execution.xml
Now you need a Process Class and a Job in the HotFolder (./config/live) of the Main JobScheduler to test the Agent.
In our example, let the agent's hostname wilma and its port 4410:
- open JOE - Job Object Editor (JobScheduler Object Editor)
Use the shortcut Ctrl-D to open the Hot Folder in JOE. You reach also this dialog from the menu File->Open Hot Folder or with the red folder icon.
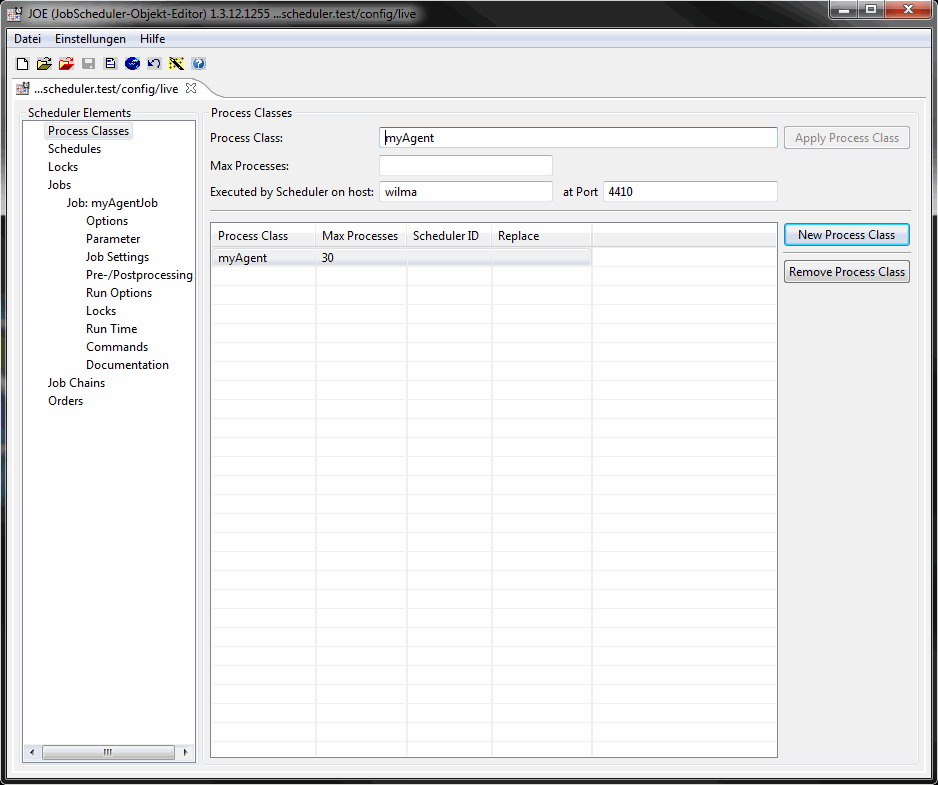
The Hot Folder should be already selected, otherwise please navigate to./config/live. - Create the process class.
Click on Process Class in the left tree of the JobScheduler elements.
With New Process Class on the right hand side you create a process class which is stored with Apply Process Class after you have enter the namemyAgentand the agent's host and portwilma:4410.
A file./config/live/myAgent.process_class.xmlis created with the content:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?> <process_class max_processes="30" remote_scheduler="wilma:4410"/>
- Create the job which uses the above process class.
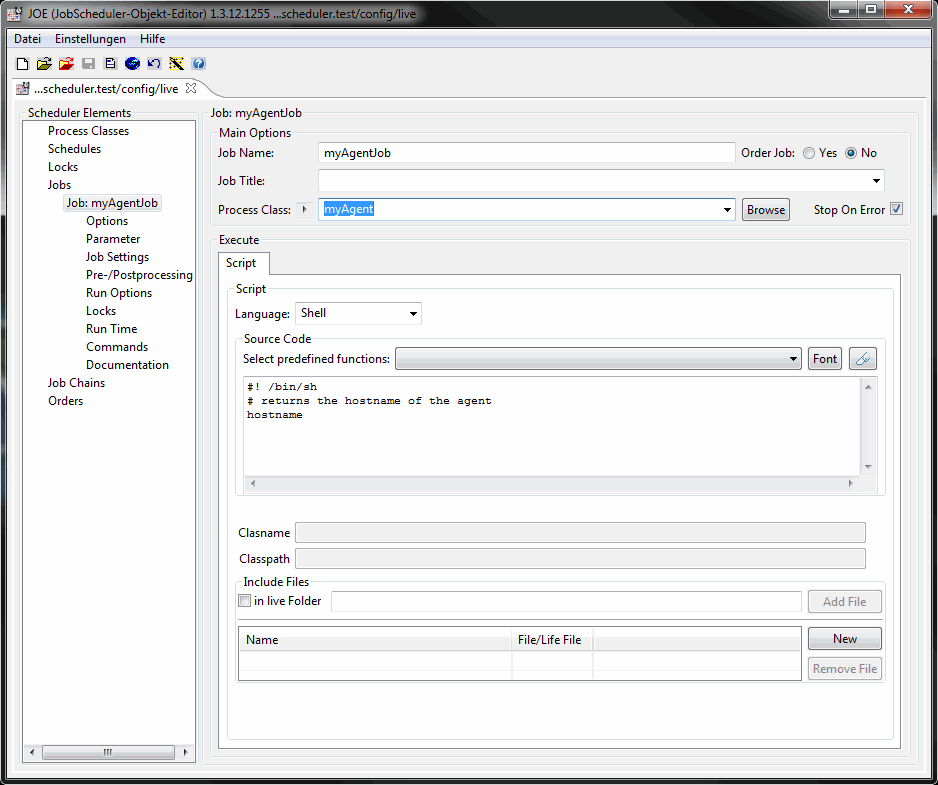
Click on Jobs in the left tree of the JobScheduler elements.
With New Standalone Jobs on the right hand side you create a new job in the list of the jobs and in the left tree. Select it to open an empty job configuration element.
Enter in the field Job Name e.g.myAgentJoband in the Source Code text area the lines:
#! /bin/sh # returns the hostname of the agent hostname
So that this job is executed on the agent, the job must be assigned to the above process class.
Set the field Process Class with the above myAgent process class.
You store this configuration with the shortcut Crtl-S or with the File->Save function.
A file ./config/live/myAgentJob.job.xml is created with the content:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<job process_class="myAgent">
<script language="shell">
<![CDATA[
#! /bin/sh
# returns the hostname of the agent
hostname
]]>
</script>
<run_time/>
</job>
The value in the process_class attribute of the job element must have a relative or absolute path to an existing process class.
Absolute path starts at the ./config/live folder.
In the above example a relative path is used and the job finds the process_class because it is stored in the same folder.
In the above example you can use the absolute path <job process_clash1. "/myAgent"> too.
For example if the job is stored in ./config/live/myProject/myAgentJob.job.xml then you can use <job process_class"/myAgent"> or <job process_class="../myAgent">.
- Start the job
myAgentJobin the JOC - Configuration and look into the task's log.
You will see a line
2011-10-10 15:26:47.237 [info] wilma