UNDER PROGRESS
Web Services
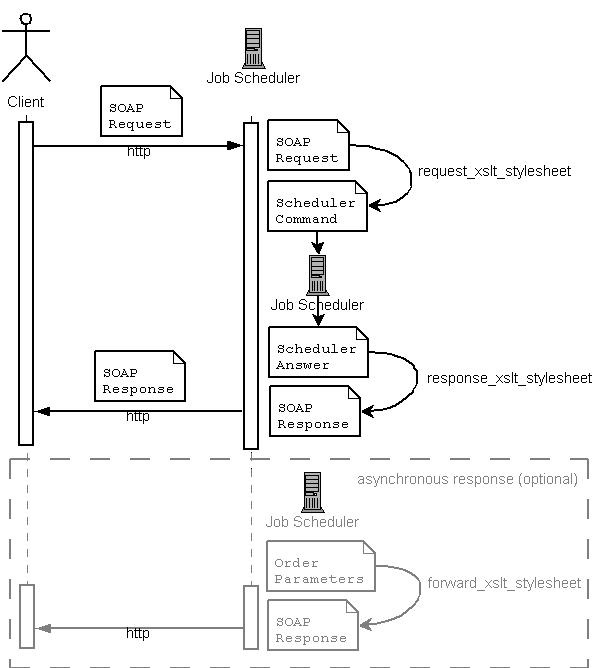
Any job or job chain in the JobScheduler can be exposed as a Web Service. The JobScheduler accept SOAP requests and send a standard SOAP response.
The JobScheduler can be configured to except start job and job chain requests either
via a generic JobScheduler Webservice interface or
<web_service ... name = "scheduler" url_path = "/scheduler" > </web_service>via specific Webservice interface for a individual job or job chain.
<web_service ... name = "start_backup" url_path = "/start_backup" > </web_service>
It is important here to differentiate between the two types of Web Service requests:
Asynchronous Web Service Requests
The Asynchronous Web Services Request feature is marked as deprecated see JS-1347 - Getting issue details... STATUS for more information.
The caller receives an acknowledgement that his request has been accepted by the JobScheduler and will be processed. Job execution is done asynchronously i.e. at a later run time. This is useful if batch jobs need execution time or should start at a predefined point in time.
No changes to job implementations are required with asynchronous Web Services processing.
Configure JobScheduler
Update
scheduler.xmlwith a generic web service interface. Following configuration will enable the JobScheduler to accept variety of SOAP requests.<http_server > <web_service debug = "no" request_xslt_stylesheet = "config/scheduler_soap_request.xslt" response_xslt_stylesheet = "config/scheduler_soap_response.xslt" name = "scheduler" url_path = "/scheduler" > </web_service> </http_server>- After
scheduler.xmlupdate to make configuration effective, restart the JobScheduler service ( Windows ) or demon ( Linux ). Now the JobScheduler is accessible via a SOAP web service. Web service can be accessed with URL
http://<jobscheduler-host>:<jobscheduler-port>/schedulere.g. http://localhost:4444/scheduler
Start a job chain
To start a job chain via SOAP web service SOAP client should send a post request to the JobScheduler with following SOAP format
- Above given SOAP request will submit a order to the job chain
example/01_JobChainShellJobs/01_JobChainA. The order will also have two parametersSOAP_PARAM1=Value1andSOAP_PARAM2=Value2, which will be passed to the job chain. SOAP request received by the JobScheduler will processed immediately and order id will be send back with response as success token.
Check Order Status
- To Check the status of order's status sent to JobSceduler send following SOAP request to the JobScheduler
Start a Job
- To start a job via SOAP web service SOAP client should send a post request to the JobScheduler with following SOAP format
- Above given SOAP request will start the job
sos/housekeeping/scheduler_rotate_log. The job will be started after 60 seconds of time of SOAP request. SOAP request received by the JobScheduler will processed immediately and task id will be send back with response as success token.
Synchronous Web Service Requests
Should a request be received by the JobScheduler then it will be instantly processed. The caller receives the job execution result on the fly. Jobs must be developed to handle this kind of request.
Configure JobScheduler
In order to user synchronous Web Service, a new Web Service needs to be created in the <web_services> element as follows and it is necessary to configure a job chain e.g. web_service_test in the scheduler.xml configuration file.
Update
scheduler.xmlwith a web service interface.<http_server > <web_service name="test" job_chain="web_service_test" url_path="/test"/> </http_server>After
scheduler.xmlupdate to make configuration effective, restart the JobScheduler service ( Windows ) or demon ( Linux ).
Configuration of a Synchronous Web Service
The following Job and Job Chain element must be configured in the JobScheduler.
Job Chain
Job
This chapter shows how a job which can read a Web Service request and return a synchronous response may be implemented.
The function of this job is the interpretation of possible protocols such as SOAP. The job receives the request content in either binary or string form. Note that in order to keep this example simple, XML will not be interpreted here, as this would make the code longer and more complicated. The use of the DOM is also not covered by this tutorial. Therefore the following job only logs the request content and returns a string containing the task ID.
The Creation of Jobs for Synchronous Web Services
This chapter shows how a job which can read a Web Service request and return a synchronous response may be implemented.
The function of this job is the interpretation of possible protocols such as SOAP. The job receives the request content in either binary or string form. Note that in order to keep this example simple, XML will not be interpreted here, as this would make the code longer and more complicated. The use of the DOM is also not covered by this tutorial. Therefore the following job only logs the request content and returns a string containing the task ID.
Following JavaScript implementation shows a simple implemented request response mechanism.
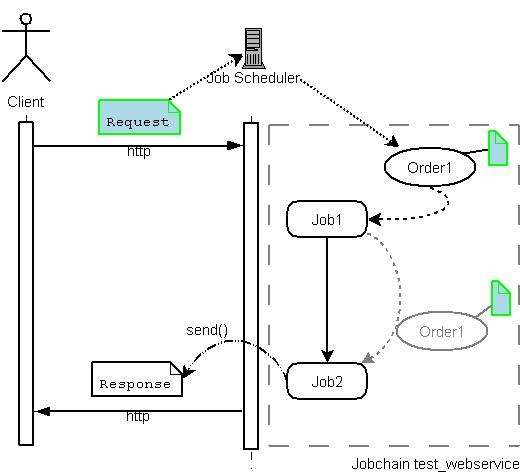
The web_service_operation() call is placed in a try-catch block at the start of the job. This is necessary as it is possible that the job has to process a order which was created by the Job Scheduler but had not been processed before the Scheduler shut down. In this case the Job Scheduler would load the order from its database although the HTTP connection to the client no longer existed. Further, the Web_service_operation object would no longer exist. The job should catch this error and decide how to handle the order.
The request content is read out of the Web_service_request object and written in the log.
The answer is added to the Web_service_response object and synchronously sent back to the client using send().
In practice the Web_service_request would be read by one job and the Web_service_response set by another. It would be possible to create a job chain in which the first job reads the Web_service_request object and evaluate and write request parameters into the order payload. Subsequent jobs would then process the order payload and only the last job would write in the Web_service_response object and call the send() method.
Change Management References