Introduction
JS7 does not make use of files for log output of order logs and task logs, see JS7 - Order Logs and Task Logs. JS7 instead streams log output from Agents to the Controller and to JOC Cockpit without use of files.
A number of users prefer to have log files available for each order execution and job execution, for example to consolidate log files on a file server or to submit log files to specific tools for log analysis.
To support a situation when log output should be consolidated to files the JS7 - REST Web Service API allows access to log output of orders and jobs. The JS7 - PowerShell Module is a lightweight wrapper for the REST Web Service API that is used for the below examples with Linux and Windows. Users are free to use the JS7 REST Web Service from their preferred scripting language to provide similar functionality.
For similar handling of order logs see JS7 - How to make order logs available from files.
Task Logs
The following cmdlets are provided:
Access Log Object
$logs = Get-JS7TaskHistory | Get-JS7TaskLog
Explanation:
- The
Get-JS7TaskHistorycmdlet returns history results that can be filtered by folders, workflows, date range, jobs, see cmdlet description. By default today's task executions are returned. - The
Get-JS7TaskLogcmdlet is used in a pipeline and returns the task log object for each history entry. - As a result the
$logsarray holds the list of task log objects.
A task log object carries a number of attributes as visible from the following console example:
PS /> $logs = Get-JS7TaskHistory | Get-JS7TaskLog
PS /> $logs[0]
controllerId : jobscheduler
agentUrl : http://apmaccs:4449
taskId : 15247
orderId : #2022-03-06#P31960629618-pdCyclicSimpleWorkflowTicking
workflow : /ProductDemo/CyclicExecution/pdCyclicSimpleWorkflowTicking
position : 0/cycle+end=1646607600000,scheme=1,i=10,next=1646564721361:2
job : job3
criticality : normal
exitCode : 0
state : @{severity=6; _text=SUCCESSFUL}
startTime : 06.03.2022 12:05:31
endTime : 06.03.2022 12:05:36
log : 2022-03-06 12:05:31.388+0100 [MAIN] [Start] Job=job3, Agent (url=http://apmaccs:4449, id=agent_002)
2022-03-06 12:05:31.795+0100 [STDOUT] using workflow: pdCyclicSimpleWorkflowTicking
running job: job3
2022-03-06 12:05:36.399+0100 [MAIN] [End] [Success] returnCode=0
Write Log to File
Get-JS7TaskHistory | Get-JS7TaskLog | Out-File /tmp/history/tasks.log -Encoding Unicode
Explanation:
Reads the logs of today's tasks and writes the logs to a common file.
Get-JS7TaskHistory -RelativeDateFrom -8h | Get-JS7TaskLog | Select-Object @{name='path'; expression={ "/tmp/history/$(Get-Date $_.startTime -f 'yyyyMMdd-hhmmss')-$([io.path]::GetFileNameWithoutExtension($_.job)).task.log"}}, @{name='value'; expression={ $_.log }} | Set-Content
Explanation:
Reads the logs of tasks that completed within the last 8 hours and writes the log output to individual files. The log file names are created from the start time and from the job name of each task.
# execute once
$lastHistory = Get-JS7TaskHistory -RelativeDateFrom -8h | Sort-Object -Property startTime
# execute in intervals
Get-JS7TaskHistory -DateFrom $lastHistory[0].startTime | Tee-Object -Variable lastHistory | Get-JS7TaskLog | Select-Object @{name='path'; expression={ "/tmp/history/$(Get-Date $_.startTime -f 'yyyyMMdd-hhmmss')-$([io.path]::GetFileNameWithoutExtension($_.job)).task.log"}}, @{name='value'; expression={ $_.log }} | Set-Content
Explanation:
Provides a mechanism to subsequently retrieve previous logs. Starting from initial execution of the
Get-JS7TaskHistorycmdlet the resulting$lastHistoryobject is used for any subsequent calls.
Consider use of theTee-Objectcmdlet in the pipeline that updates the$lastHistoryobject that can be used for later executions of the same pipeline.This pipeline can e.g. be executed in a cyclic job.
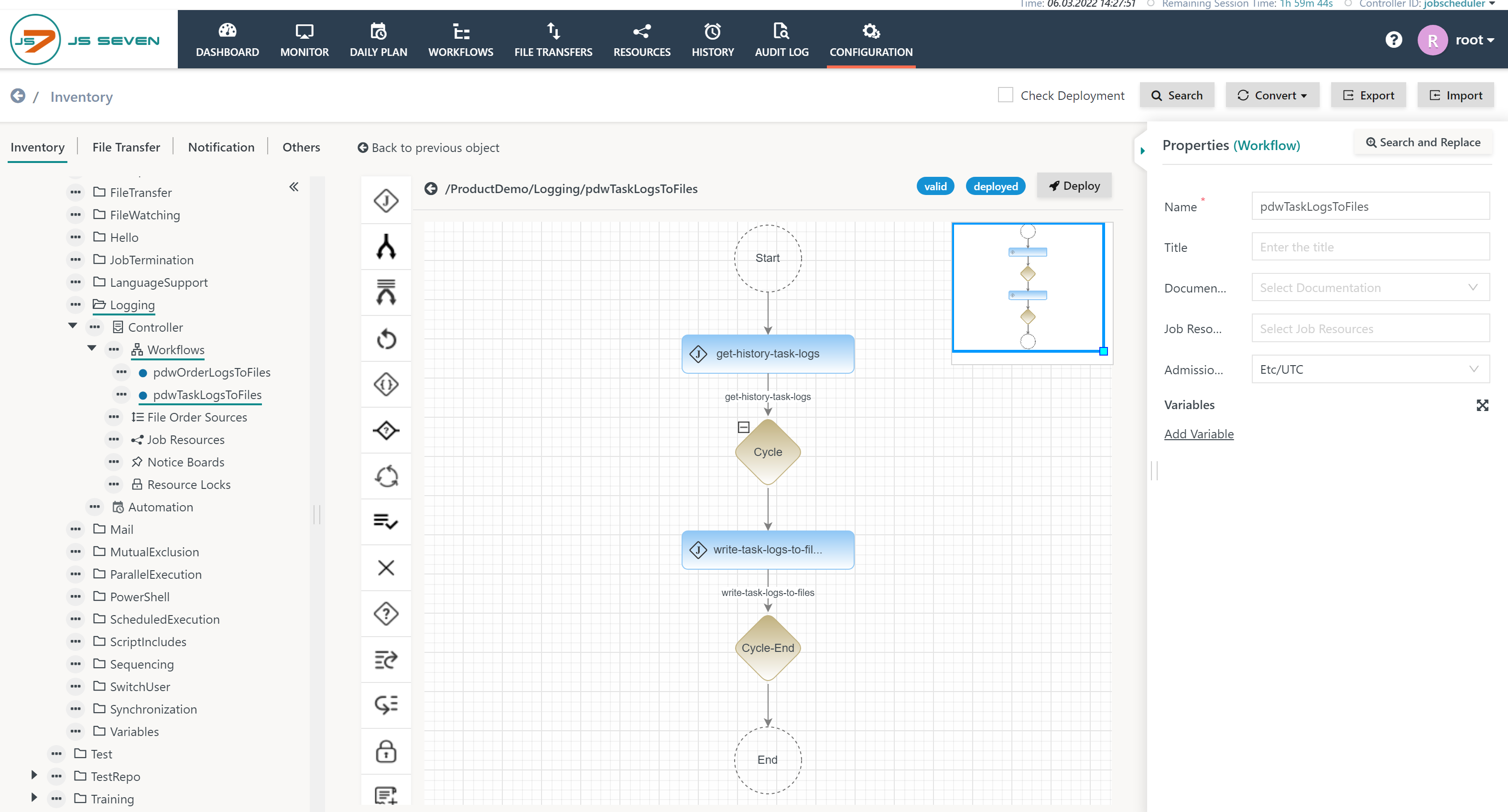
Automate Log File Creation
A workflow is created that runs the above commands in a cycle. The workflow operates 24/7 and writes task logs to files.
Download: pdwTaskLogsToFiles.workflow.json
Explanation:
- The first job
get-history-task-logsis executed at the point in time when the order arrives that starts the workflow.- This job determines the last history entry from which to start.
- The second job
write-task-logs-to-filesis executed within a JS7 - Cycle Instruction:- The above example implements a ticking cycle every 30 minutes. For a 24h period the job will repeat every 30 minutes.
- Users can adjust the cycle at their will.
The first job get-history-task-logs looks like this:
#!/usr/bin/env pwsh
Import-Module JS7
Connect-JS7 -Url http://root:root@localhost:4446 -Id Controller | Out-Null
$lastHistory = Get-JS7TaskHistory -RelativeDateFrom -30m | Sort-Object -Property startTime
# serialize and base64 encode the object
$xmlLastHistory = [management.automation.psserializer]::Serialize( $lastHistory )
$lastHistoryEncoded = [System.Convert]::ToBase64String([System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetBytes( $xmlLastHistory ))
# forward a variable for the object
"lastHistoryEncoded=$lastHistoryEncoded" | Out-File $env:JS7_RETURN_VALUES -Append
Disconnect-JS7
Explanation:
- Line 1: The shebang is required to identify PowerShell being the interpreter of the script. The above example is for Unix, for Windows the first line of the job script should be replaced as follows:
- Example of shebang for PowerShell with Unix
#!/usr/bin/env pwsh
- Example of shebang for PowerShell with Windows
@@findstr/v "^@@f.*&" "%~f0"|pwsh.exe -&goto:eof
- Line 4: The are a number of ways how to specify details for a JS7 connection, see JS7 - How to connect to JOC Cockpit using the PowerShell Module.
- The host and port are specific for a user's environment.
- The Controller ID is specified during installation of the Controller and defaults to
Controller.
- Line 9-13: A variable is created that carries the History ID of the latest entry for which task logs should be created. This variable is in fact a PowerShell object that is serialized and base64-encoded for use with the second job in the workflow.
The second job write-task-logs-to-files looks like this:
#!/usr/bin/env pwsh
Import-Module JS7
Connect-JS7 -Url http://root:root@localhost:4446 -Id Controller | Out-Null
# bas64 decode and deserialize the object
$xmlLastHistory = [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String( $env:LAST_HISTORY_ENCODED ))
$lastHistory = [System.Management.Automation.PSSerializer]::Deserialize( $xmlLastHistory )
Get-JS7TaskHistory -DateFrom $lastHistory[0].startTime | Tee-Object -Variable lastHistory | Get-JS7TaskLog | Select-Object @{name='path'; expression={ "/tmp/history/$(Get-Date $_.startTime -f 'yyyyMMdd-hhmmss')-$([io.path]::GetFileNameWithoutExtension($_.job)).task.log"}}, @{name='value'; expression={ $_.log }} | Set-Content
# serialize and base64 encode the object
$xmlLastHistory = [management.automation.psserializer]::Serialize( $lastHistory )
$lastHistoryEncoded = [System.Convert]::ToBase64String([System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetBytes( $xmlLastHistory ))
# forward a variable for the object
"lastHistoryEncoded=$lastHistoryEncoded" | Out-File $env:JS7_RETURN_VALUES -Append
Disconnect-JS7
Explanation:
- Lines 1, 4: Same explanations as for the previous job.
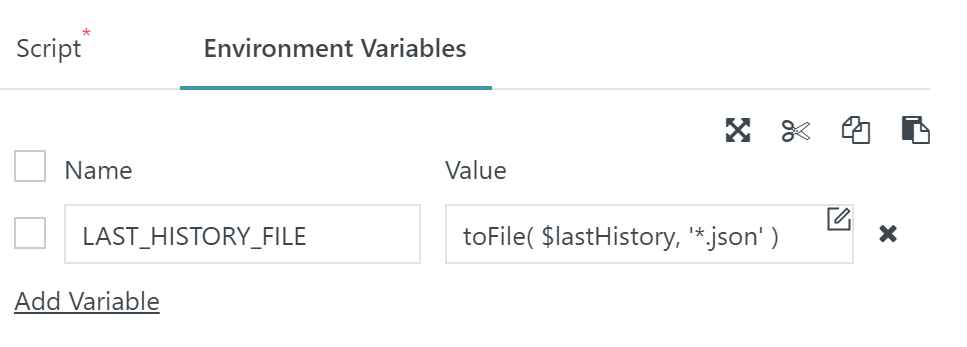
- Lines 7,8: The History ID of the last processing of this job is picked up from an environment variable that is assigned the workflow variable previously serialized and base64-encoded.
Line 10: When reading the task history then the variable carrying the History ID is updated and is forwarded to the workflow for next execution of the cycle.