work in progress
Article under construction
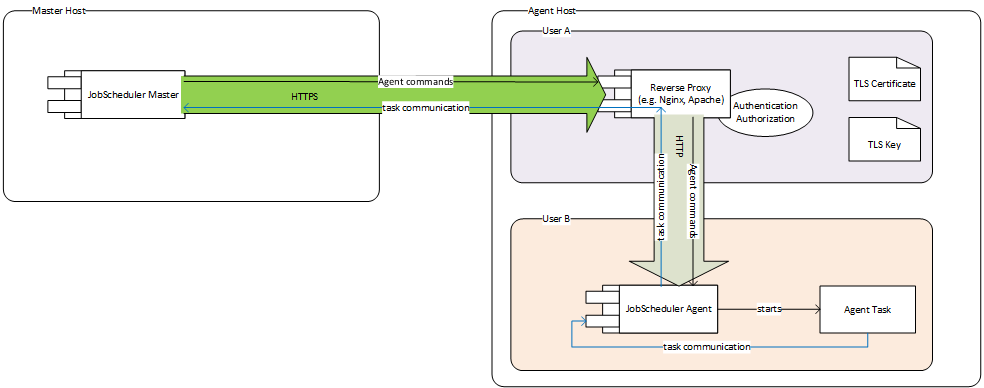
Communication to and from the Java Based Agent can be secured by HTTPs using a 3rd party proxy (e.g. apache http server, nginx).
This setup needs 2 users on the agent server:
- User A
- has access to the SSL certificate and the SSL key
- has access to the proxy server configuration files
- executes the proxy server, which is configured to
- allow connections by HTTPs (using the SSL certificate and key)
- allow connections only from certain IPs
- proxy these connections to JobScheduler Agent on localhost
- User B
- does not have access to the SSL certificate and the SSL key
- does not have access to the proxy server configuration files
- executes the JobScheduler Agent which is parameterized to
- only allow connections on the local network interface
All communication between the JobScheduler Master server and the Agent server goes through an HTTPs connection
- JobScheduler Master requests a job start on the Agent
- the request goes through https to the proxy
- the proxy forwards the request by http to JobScheduler Agent the same machine
- JobScheduler Agent starts an agent task
- The agent tasks commuicates with JobScheduler Master (logging, api calls...)
- the agent task connects on port 59999 or lower to the JobScheduler Agent
- JobScheduler agent uses the existing HTTP connection to the proxy continuing in an HTTPs connection to JobScheduler master to relay communication from the agent task to JobScheduler master
motivation for using a 3rd party proxy
- Separation of confidential credentials from JobScheduler Agent
- Whoever is able to run jobs JobScheduler Agent is able to
- access all files that can be accessed by the user running JobScheduler Agent
- execute all processes that can be executed by the user running JobScheduler Agent
- do whatever the user running JobScheduler Agent could do on the shell
- If the user running JobScheduler Agent was the same user that runs the proxy (or if the proxy was integrated into JobScheduler Agent), he could
- steal the SSL key
- reconfigure the proxy to accept connections from other hosts
- Whoever is able to run jobs JobScheduler Agent is able to
- The Java Based JobScheduler agent aims at a zero-configuration approach
- Setting up SSL encryption needs a lot of configuration (certificates, keys, protocol options)
- Experienced adminstrators know how to configure this in the proxy of their choice (but would have to learn how to do this if it was configured in JobScheduler Agent)
- Use existing trusted functionality
- SSL configuration and handling
- Authentication: simple authentication can be achieved by restricting proxy access to certain hosts
- Authorisation: proxy servers can be configured to allow
- GET and POST requests for some hosts → execution of jobs possible
- only GET request for other hosts → read-only access (status information...)
security
This setup secures the agent against:
- attackers eavesdropping on the network
- attackers using JobScheduler agent to steal the SSL certificate and key
- attackers using JobScheduler agent to reconfigure the authentication in the proxy
- attackers spoofing the identity of the agent server
- attackers trying to control the agent from other IPs
This setup does not secure the agent against:
- attackers spoofing the IP of the Master JobScheduler
possible enhancements
Validating the client identitiy using HTTPs client authentication
- JobScheduler Master is configured with a client HTTPs certificate
- The proxy is configured to only accept connections with a valid client certificate