Page History
| SEO Metadata | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
JS7 brings a security architecture based on certificates for connections between products and for digital signing of workflows and jobs |
| Table of Contents |
|---|
Introduction
| Table of Contents |
|---|
...
- The Security Architecture includes:
- Secure Communication:
- Certificate Management: Create and deploy certificates for secure network communication between componentsproducts.
- Life Cycle Management: Create, update and delete certificates and deploy changes to componentsproducts.
- Secure Configuration:
- Configurations include workflows, jobs and related objects.
- Such These objects are digitally signed and deployed by a responsible person.
- Secure Operation:
- Access Management: Authentication and Authorization via LDAP Directory Servicea LDAP, OIDC, Certificates, FIDO etc.
- Credential Management: Use of a Credential Store for confidential data.
- Secure Communication:
- Wording
- The term Deployment applies to a situation that when a configuration is transferred from the JOC Cockpit to a MasterController and Agents.
- The term Roll-out applies to a situation that when a configuration is transferred between environments, e.g. from dev to test and to prodfor example from non-production to production environments. Within the respective target environment a Deployment is performed to transfer configuration objects to Masters Controllers and Agents.
Security Architecture
- Download: JS7_JobScheduler_Security_Architecture.pptx
- Download: JS7_JobScheduler_Security_Architecture.pdf
- Download Use the links above to download the slides from above links should , if the display of the document below document does not work for in your browser:
|
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
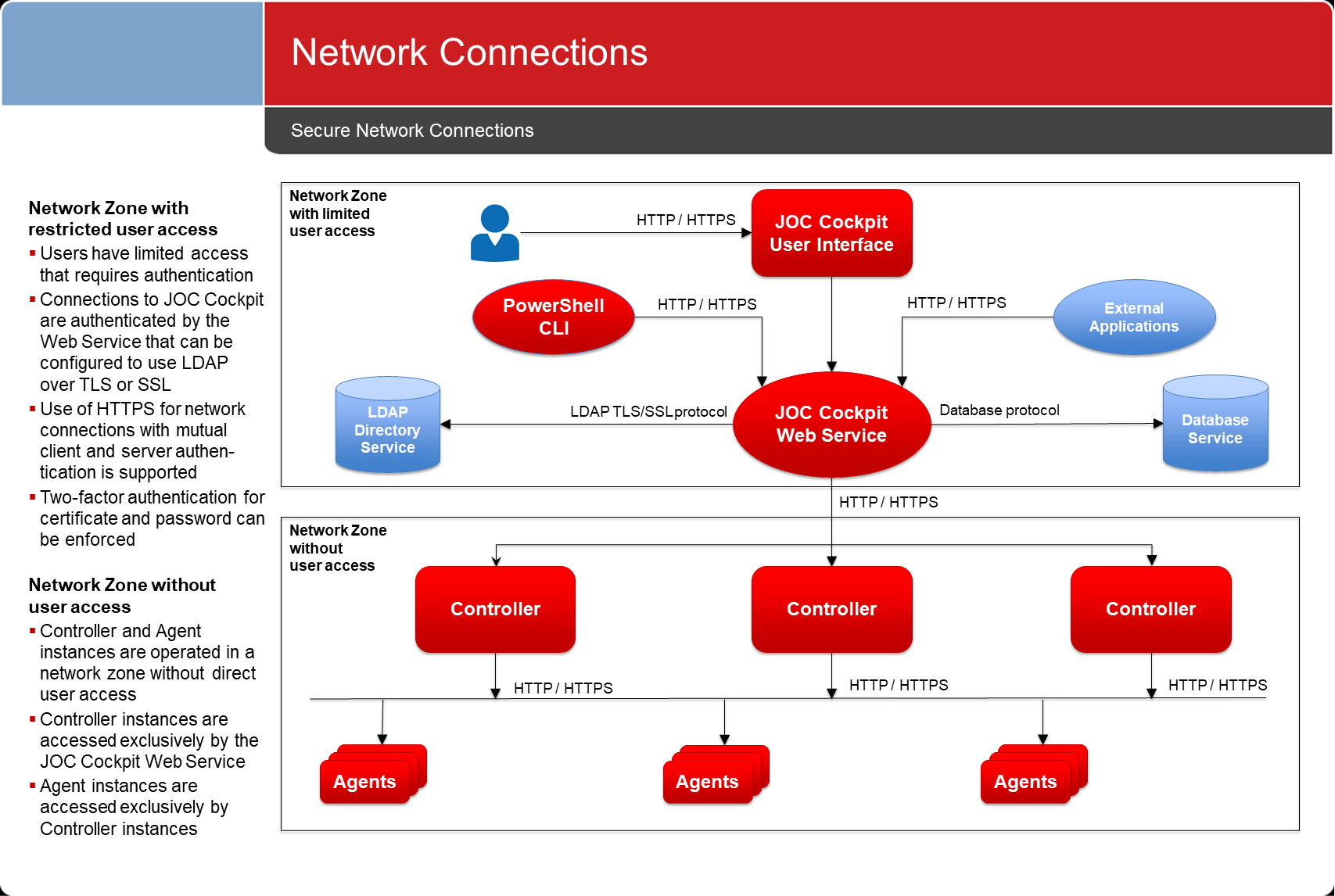
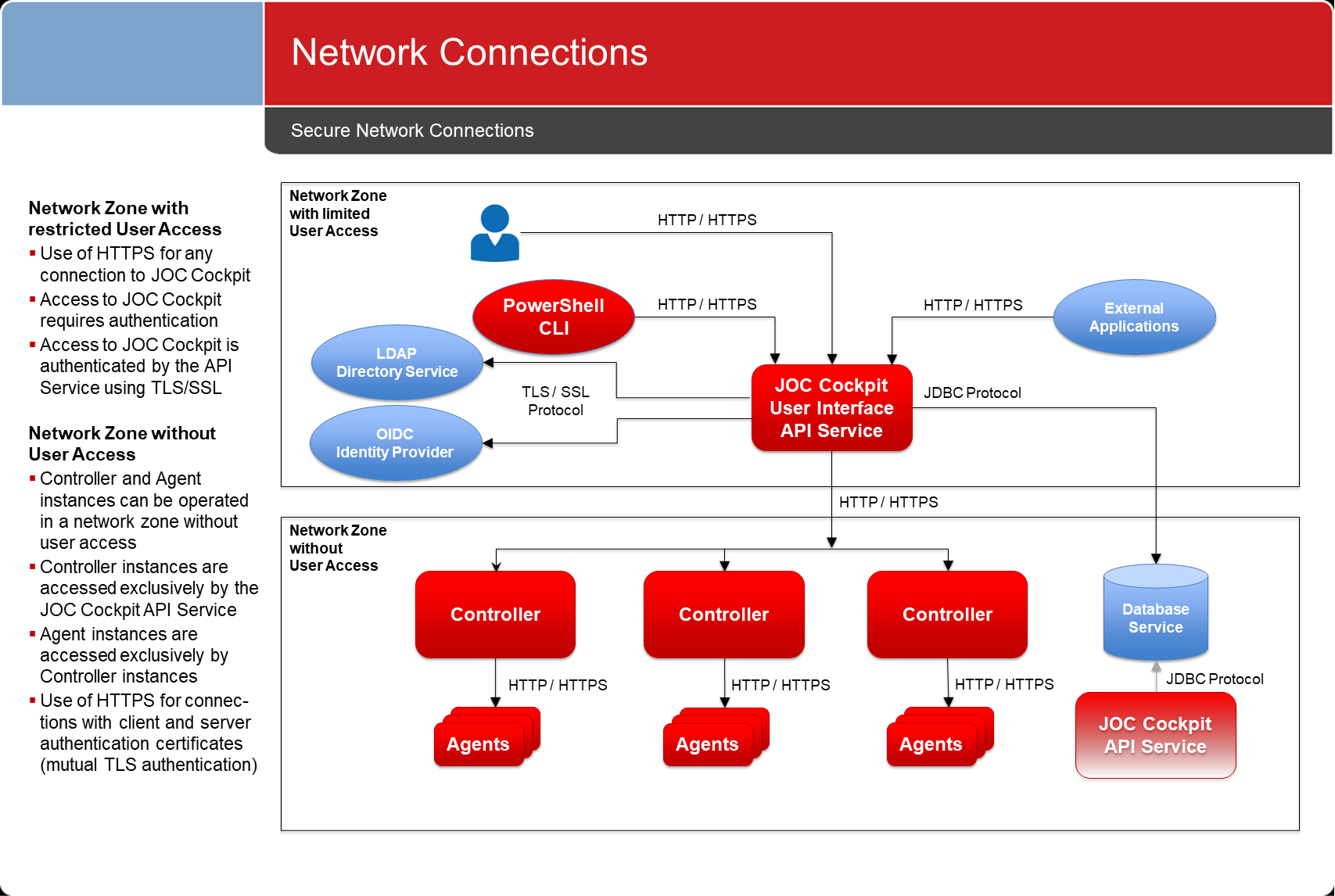
Network Connections
- Network connections between components use products use the HTTPS protocol.
- Such connections are secured by x509 certificates, by default using mutual client and server authentication.
- Connections are established in one direction only.
Certificate Management
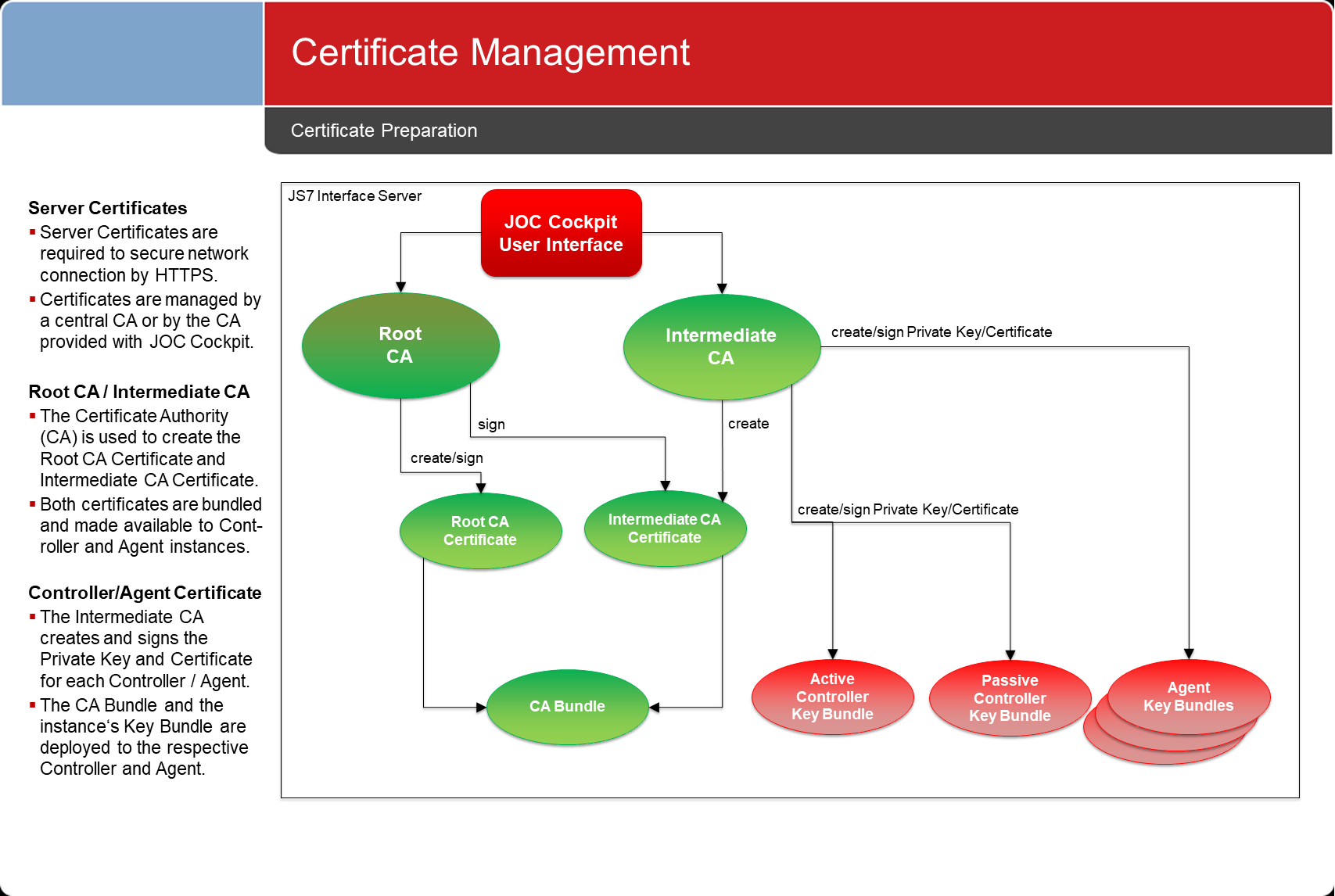
Certificate Preparation
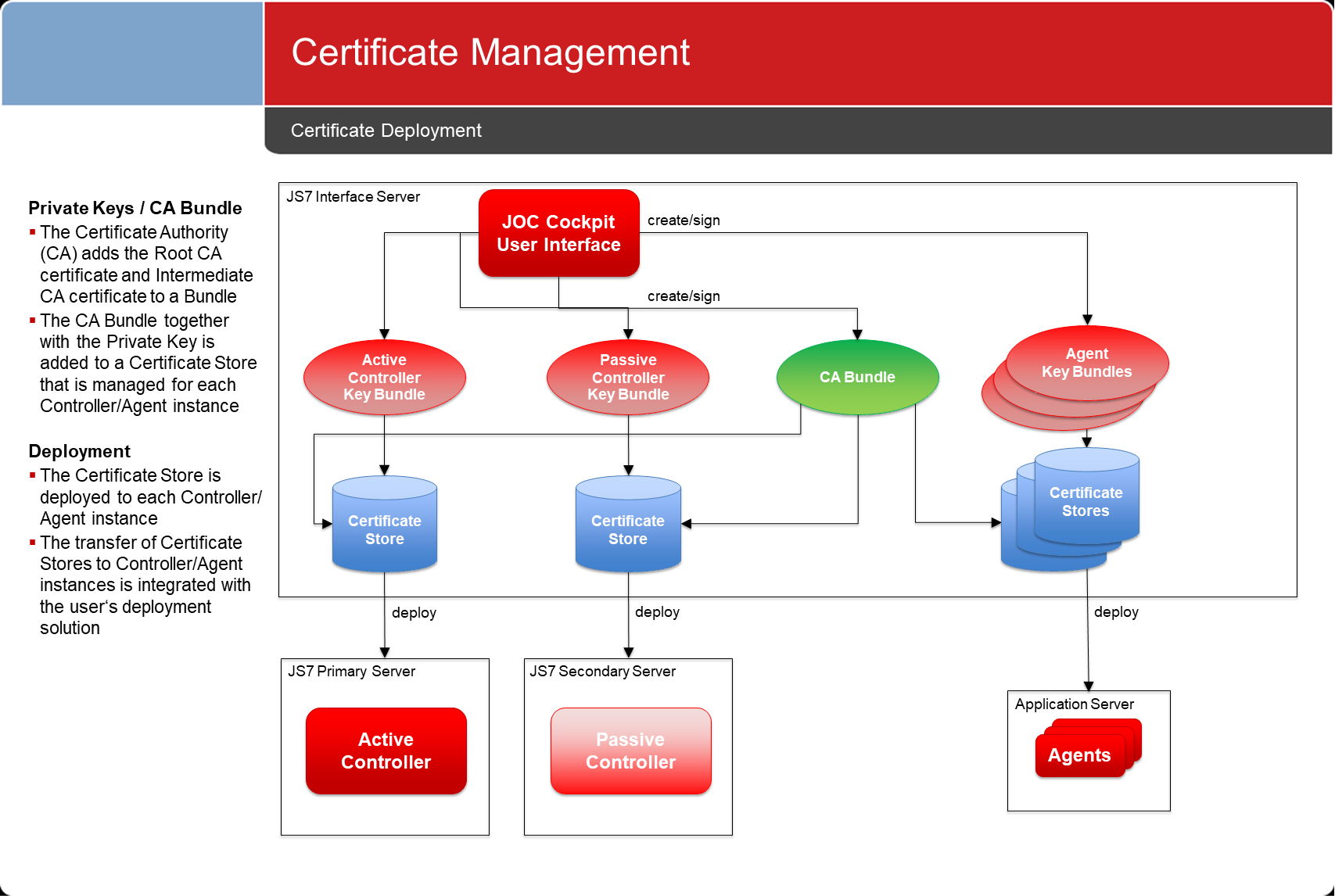
Certificate Deployment
Certificate Management Life Cycle
Certificate Preparation
- Certificates are created:
- either from a CA independently from JS7,
- This applies to users of JS7 who require high security levels the "high" Security Level and therefore operate a CA on of their own.
- or directly from the the JS7 - Certificate Authority in JOC Cockpit.
- This applies to users of JS7 who prefer a modest security level "low" or "medium" Security Level without the effort of maintaining a CA.
- The JOC Cockpit implements:
- a Root CA and Intermediate CA to create certificates for JS7 componentsproducts.
- deployment capabilities to prepare the security configuration for JS7 componentsproducts, i.e. to generate keystores and truststores that which the relevant certificates are added the respective certificatesto.
- either from a CA independently from JS7,
- Certificates can be maintained with JOC Cockpit should no if an individual CA be is not in place.
- Private Keys and Certificates are stored with the JS7 database.
- A user interface is available for any operations on certificates, such as creating, updating and deleting certificates.
- Certificates are prepared for deployment:
- For each JS7 component such as Masters and Agents a A keystore and truststore is created that holds to hold the required certificates is created for individual JS7 products such as Controllers or Agents.
- Keystores and truststores can be forwarded to Masters Controllers and Agents by any suitable means, e.g. for example by file transfer, SSH, transportable disks etc.
- Keystores and truststores can be imported to Masters Controllers and Agents by use of using a shell script.
Certificate Revocation
- Certificates are revoked by deploying updated certificates.
- Support for Certificate Revocation Lists (CRL) can be added at a later point in time if such demand occursis not in place.
- The Java architecture and certificate types allow implementation of a CRL.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
- Configurations include any all deployable scheduling objects that are used for job execution with Agents, such as workflows, jobs etc.
- Basically the deployment of jobs that include e.g. The jobs deployed to Agents can include calls to OS commands, scripts and binaries, to any Agents . Such deployments should be considered as a code injection to a remote machine that requires requiring authentication and authorization.
- Therefore a configuration is scheduling objects are required to be signed by a responsible person:
- this This guarantees that workflows, jobs etc. are authorized for deployment by individuals who are in charge of this task.
- this This guarantees non-repudiability of deployments.
- JOC Cockpit offers different security levels Security Levels for deployment tasksof scheduling objects.
Secure Deployment
- To deploy configuration objects includes to transfer e.g. workflows and jobs scheduling objects to a Master Controller in a given environment includes transferring objects such as workflows and jobs.
- This step can be simplified for e.g. development environments, when frequent changes occur to configuration scheduling objects and deployments are performed with a single mouse click.
- This step can be more complex if a sharing of responsibilities is included, e.g. to roll-out configuration duties is in place, for example, when rolling-out scheduling objects from a development environment to a test or production environment. This situation is called a roll-out and is explained with in the subsequent chapter.
- A secure deployment matches the security requirements in a given environment. Therefore the JOC Cockpit can be operated in with different Security Levels.
- Security Levels "lowLow" and "medium" Security Levels allow simplified deployment and are suitable for environments with modest security requirements.
- Security Level The "high" Security Level takes more effort and is targeted towards organisations organizations with more elaborate security requirements.
- Security Levels are put in place during the installation of the JOC Cockpit. Each instance of the JOC Cockpit can be operated in one of the Security Levels onlyonly operated at a single Security Level. There is no fallback from a Security Level "high" to a "medium" or "low" security levelSecurity Level. Changing the Security Level requires to reinstall reinstalling JOC Cockpit.
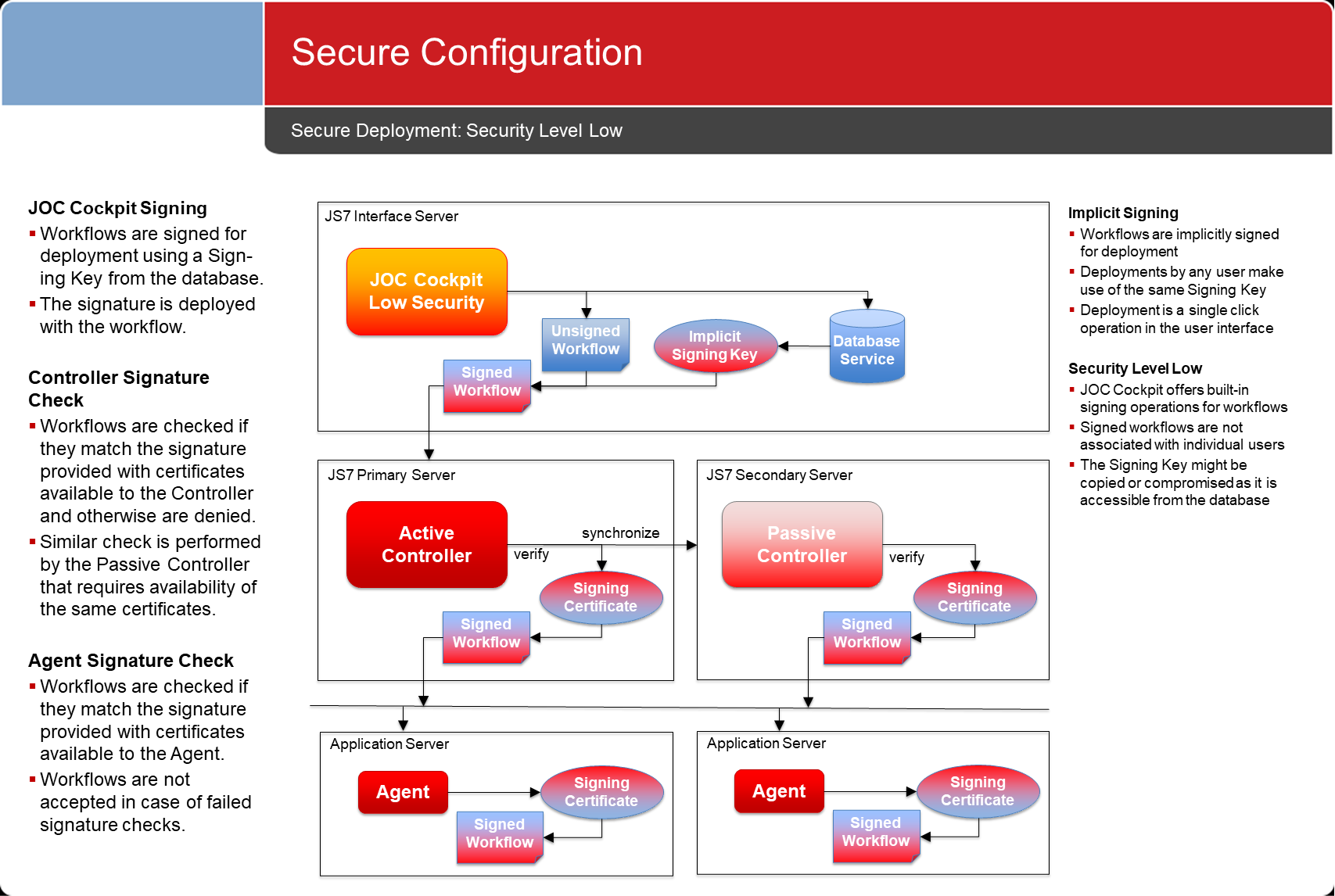
Security Level Low: Implicit Signing
- Any configuration Configuration objects are automatically signed by JOC Cockpit. This task is performed implicitly when deploying objects.
- This mechanism is easy to use from a single-click operation as signing operations are performed without user interaction.
- At the same time there is no certainty about who has deployed objects, as any user who is authorized to deploy objects can use the respective deploy functionality from relevant deployment function with a single mouse click.
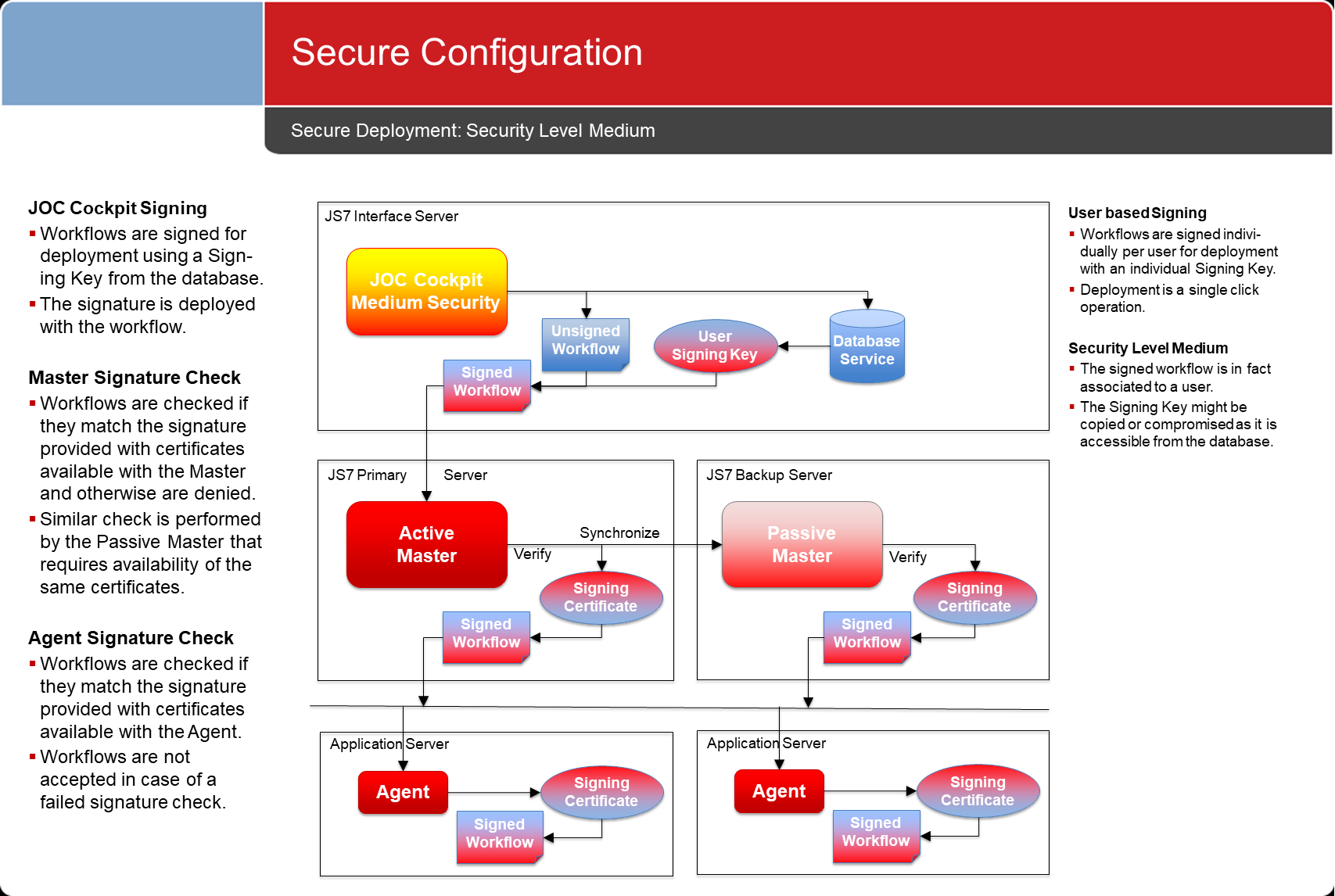
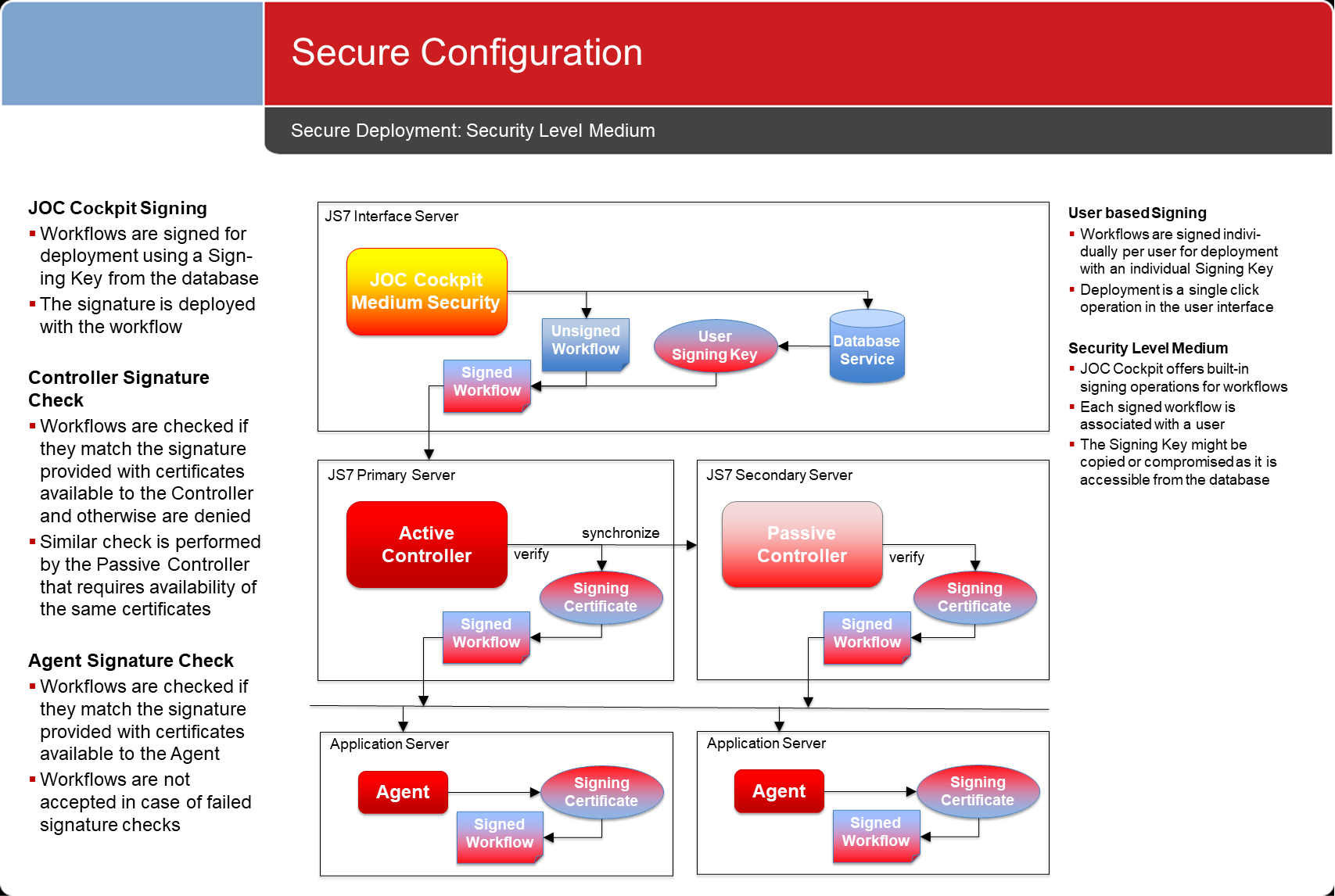
Security Level Medium: User based Signing
- Configuration objects are signed individually with the private key of the user. This applies within the scope of permissions used in JOC Cockpit to authorize individual accounts for deploying configuration objects.
- This mechanism is similar to implicit signing except for the fact that the private key stored with the current user's profile is used.
- Consider Note that similar similarly to implicit signing, all private and public keys of users are stored in a database and therefore are accessible to a DBA or system administrator.
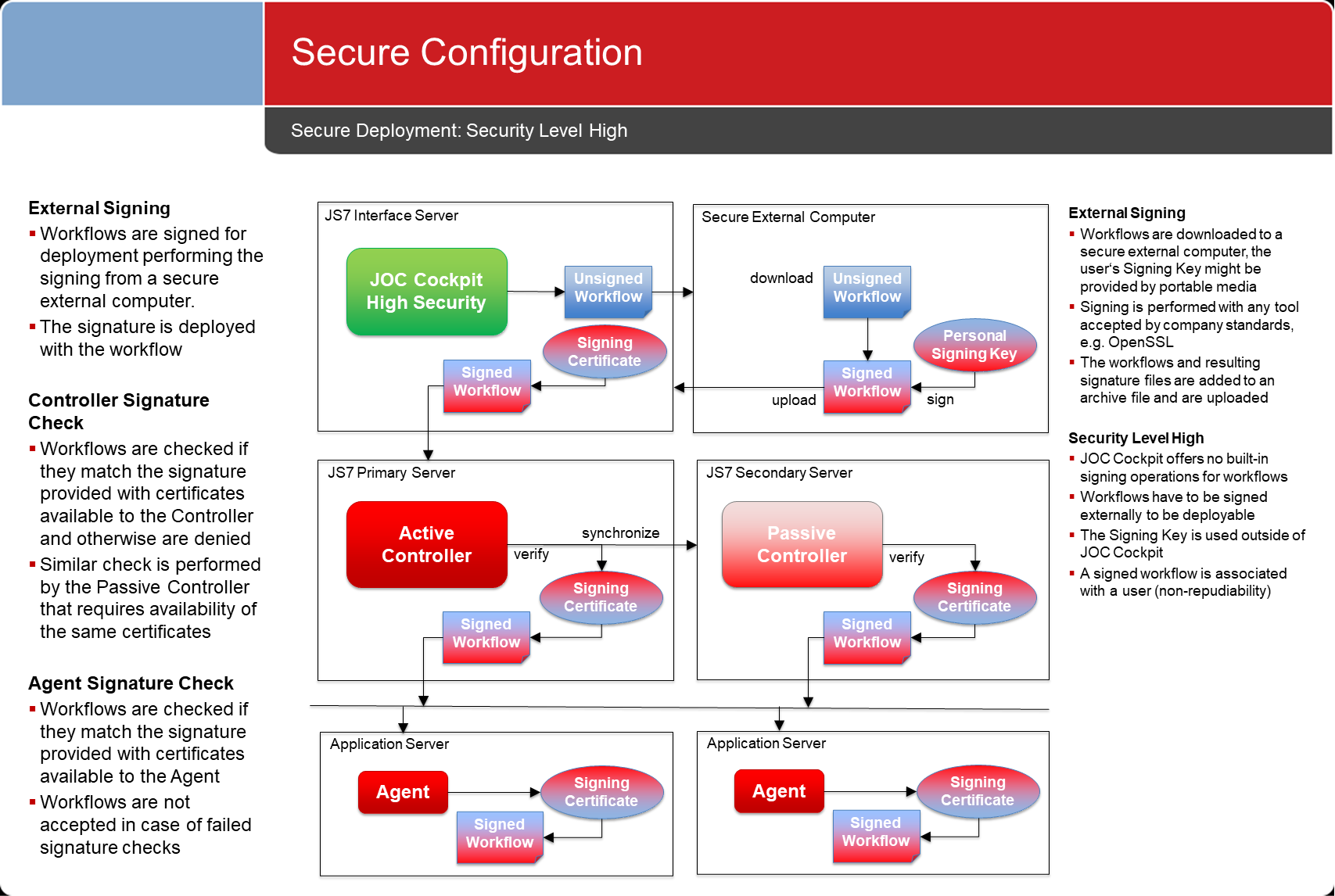
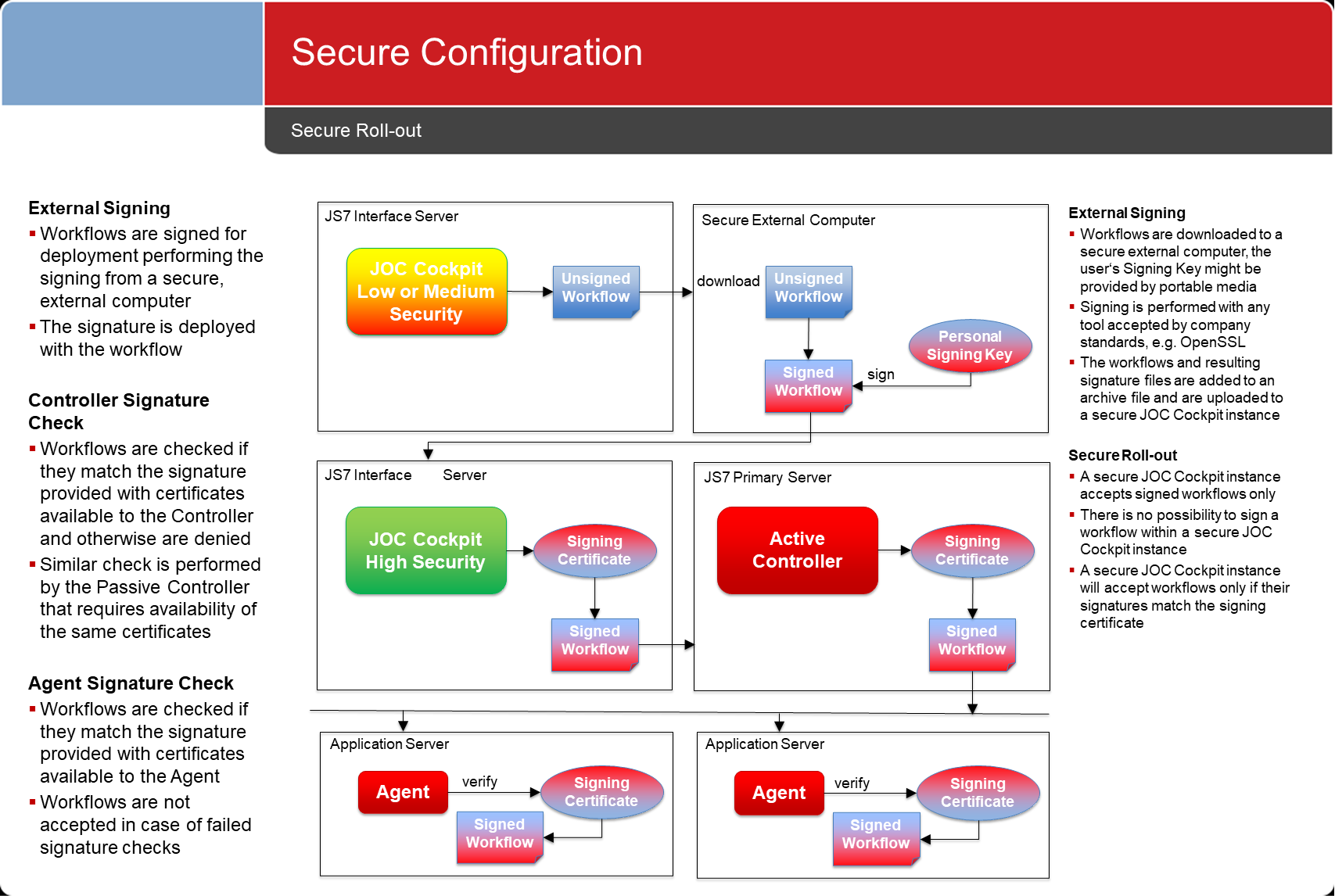
Security Level High: External Signing
- The security level requires any configuration objects to be exported and to be signed individually outside of the JOC Cockpit.
- This guarantees that at no any point in time, the JOC Cockpit has any no knowledge about the private key used for signing.
- Security has a price: there is some effort required to export a configuration, to sign it and to import the signed configuration.
Secure Roll-out
- A roll-out includes to transfer transferring configuration objects between environments, e.g. for example from development to test and to production environments.
- Steps for a roll-out include considering:
- that the roll-out might include shared responsibilities, e.g for example being performed by an individual that is different from the person who managed the configuration, e.g.a different individual to the one who manages the configuration. For example:
- a developer would will create workflows and jobs in a development environment and deploy them to Masters Controllers and Agents in that environment.
- an application manager would will perform some quality assurance and pick up configurations from a development environment for roll-out to a test environment
- a release manager would will authorize roll-out from a test environment to a production environment.
- to export that when exporting a configuration, the affected configuration objects are downloaded to a single archive file (.zip, .tar.gz)
- to sign the downloaded configuration objects that should Security Level High be in place including , then signing the downloaded configuration objects will include the tasks:
- to transfer transferring the downloaded archive to a secure environment, e.g. for example to a computer that is separated from the network.
- to extract extracting the archive to disk and to use a program that applies to company proven standards to sign signing the files included with the archive. This step includes that the user's private key is being used to sign files. As a result a signature file is created for each file extracted from the archive a signature file is created.
- to add adding the extracted files and the signature files to an archive file.
- to transfer that the archive with signed files has to be transferred to the target environment. This includes to use using any means for file transfer such as copying between servers, use of SCP, SFTP etc.
- to import that the archive with signed files has to be imported to JOC Cockpit in the target environment.
- that the roll-out might include shared responsibilities, e.g for example being performed by an individual that is different from the person who managed the configuration, e.g.a different individual to the one who manages the configuration. For example:
- The final step includes to deploy deploying the imported and signed configuration objects to the target environment.
- This task can be performed by the same individual who signed and transferred the archive file or this can require a separate role in the JOC Cockpit to be authorized to deploy in the target environment.
...
- Access Management includes access to JOC Cockpit and to the REST Web Service API. This applies to both users who access the JOC Cockpit GUI and to & scripts, and applications that directly access the REST Web Service API.
- The JobScheduler Master Controller is assumed not to be accessed by users directly but exclusively via the JOC Cockpit REST Web Service API. No default authentication is provided if the insecure HTTP protocol is used.
- JobScheduler Universal Agents are assumed not to be accessed by users directly but exclusively by a JobScheduler MasterController. No No default authentication is provided .
Roles and Permissions
Default Configuration
- The JOC Cockpit REST Web Service ships with a default configuration in
./joc/resources/joc/shiro.inithat includes- using local authentication with accounts and passwords stored as hash values,
- using local role assignment,
- the following default values for accounts, passwords and assigned roles (see JOC Cockpit - Authentication and Authorization for more information):
administrator=secret, administratorapplication_manager=secret, application_managerit_operator=secret, it_operatorincident_manager=secret, incident_managerbusiness_user=secret, business_userapi_user=secret, api_userroot=root, all
Secure Configuration
...
- if the insecure HTTP protocol is used.
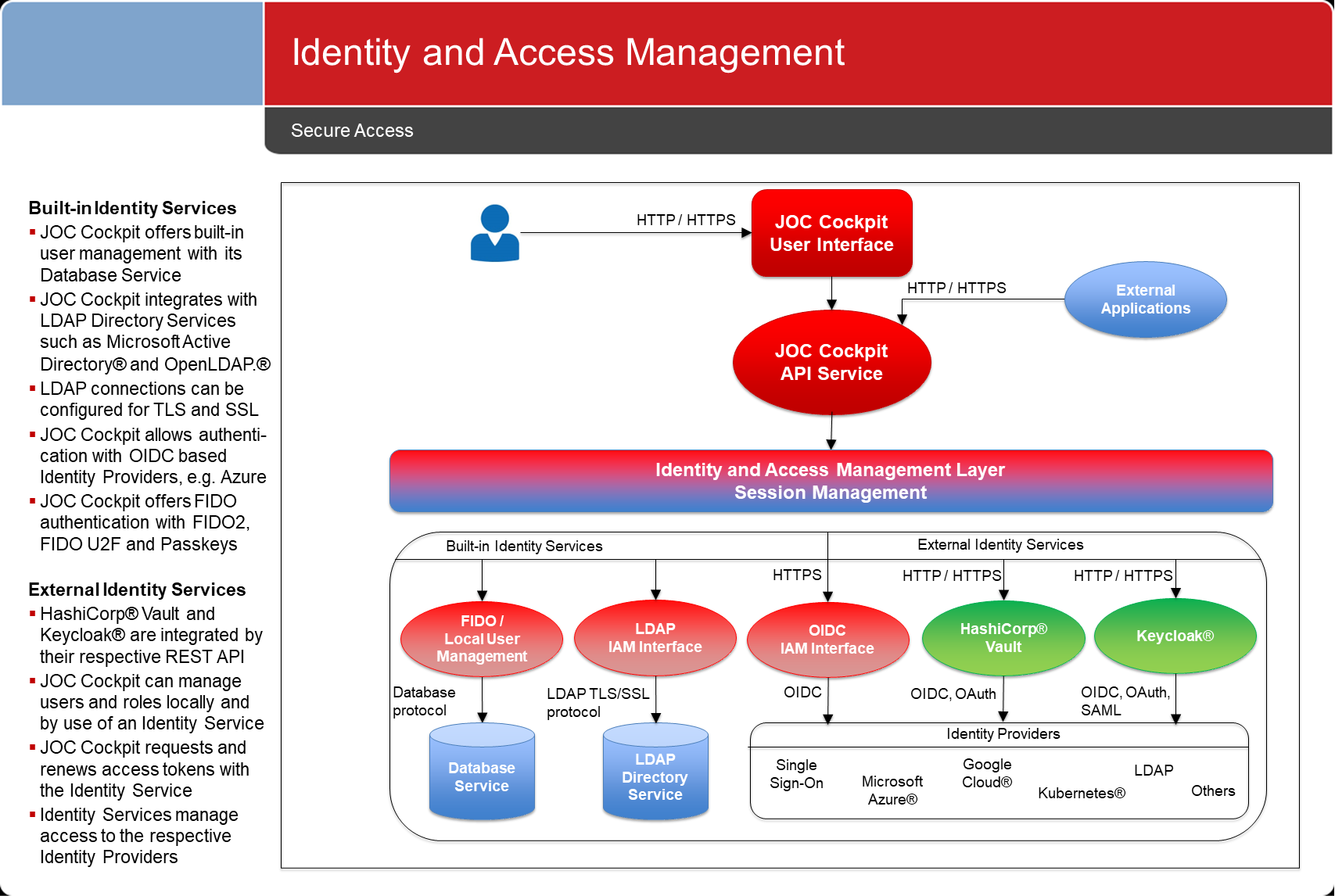
Access to JOC Cockpit is subject to authentication and authorization.
JOC Cockpit implements a number of JS7 - Identity Services:
- Identity Services with built-in support for local user management, LDAP, OIDC, Certificates, FIDO.
- Identity Services for use with external Identity Providers such as Keycloak®, HashiCorp® Vault
JOC Cockpit offers Role Based Access Management, see JS7 - Authorization
- Permissions for operations in the GUI and in the JS7 REST Web Service API
...
- can freely be grouped to roles.
...
LDAP Directory Service
Default Configuration
- It is not recommended to use the default configuration with local authentication for the JOC Cockpit REST Web Service.
Secure Configuration
...
- Users are assigned roles.
Identity Services
JOC Cockpit offers a number of Identity Services for authentication and authorization:
...
Credential Management
Database Credentials
Default Configuration
- No default values are provided by the installer.
Secure Configuration
...
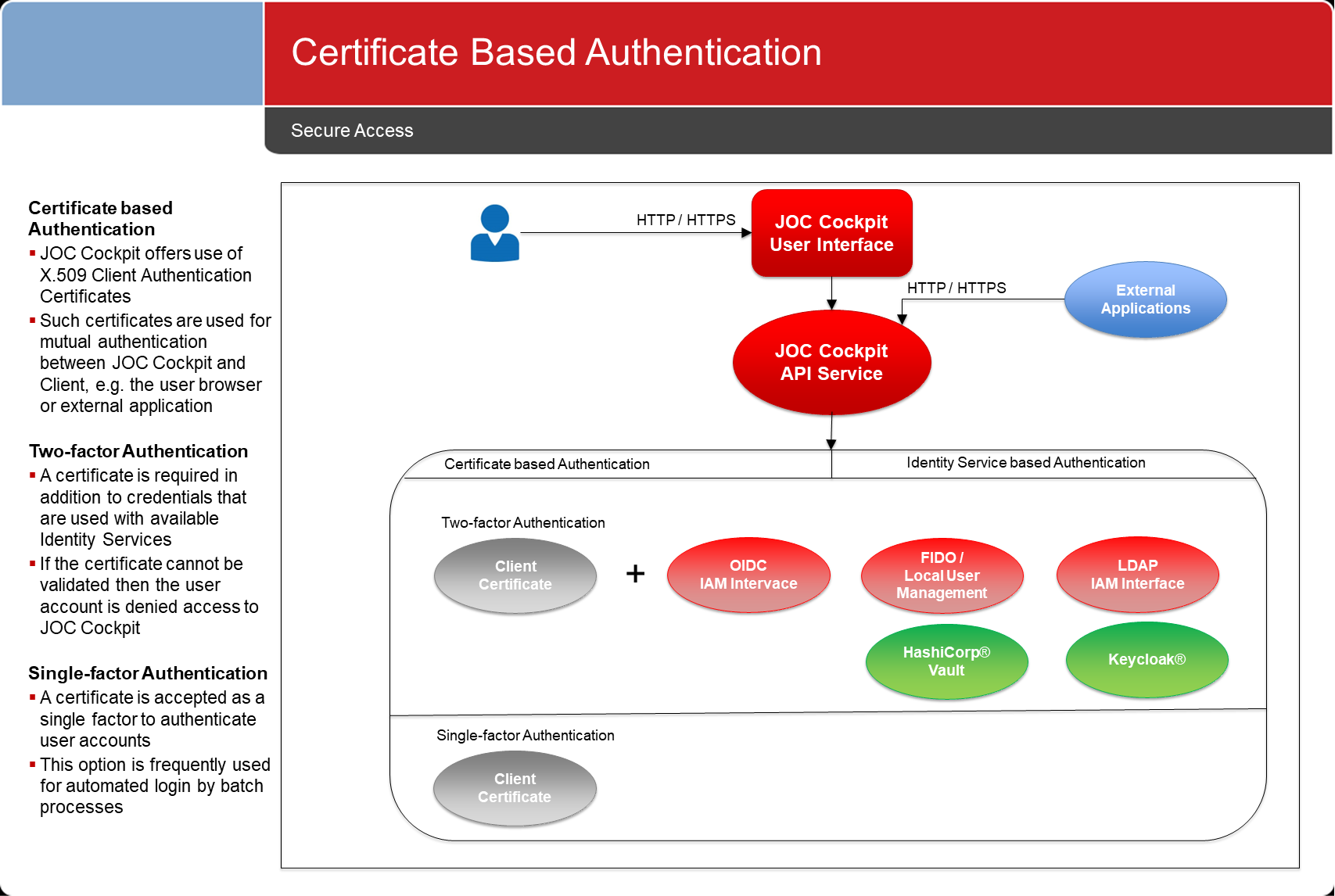
Certificate Based Authentication
Certificates can be used as a single factor for authentication or as a second factor (MFA). For details see JS7 - Certificate Identity Service.
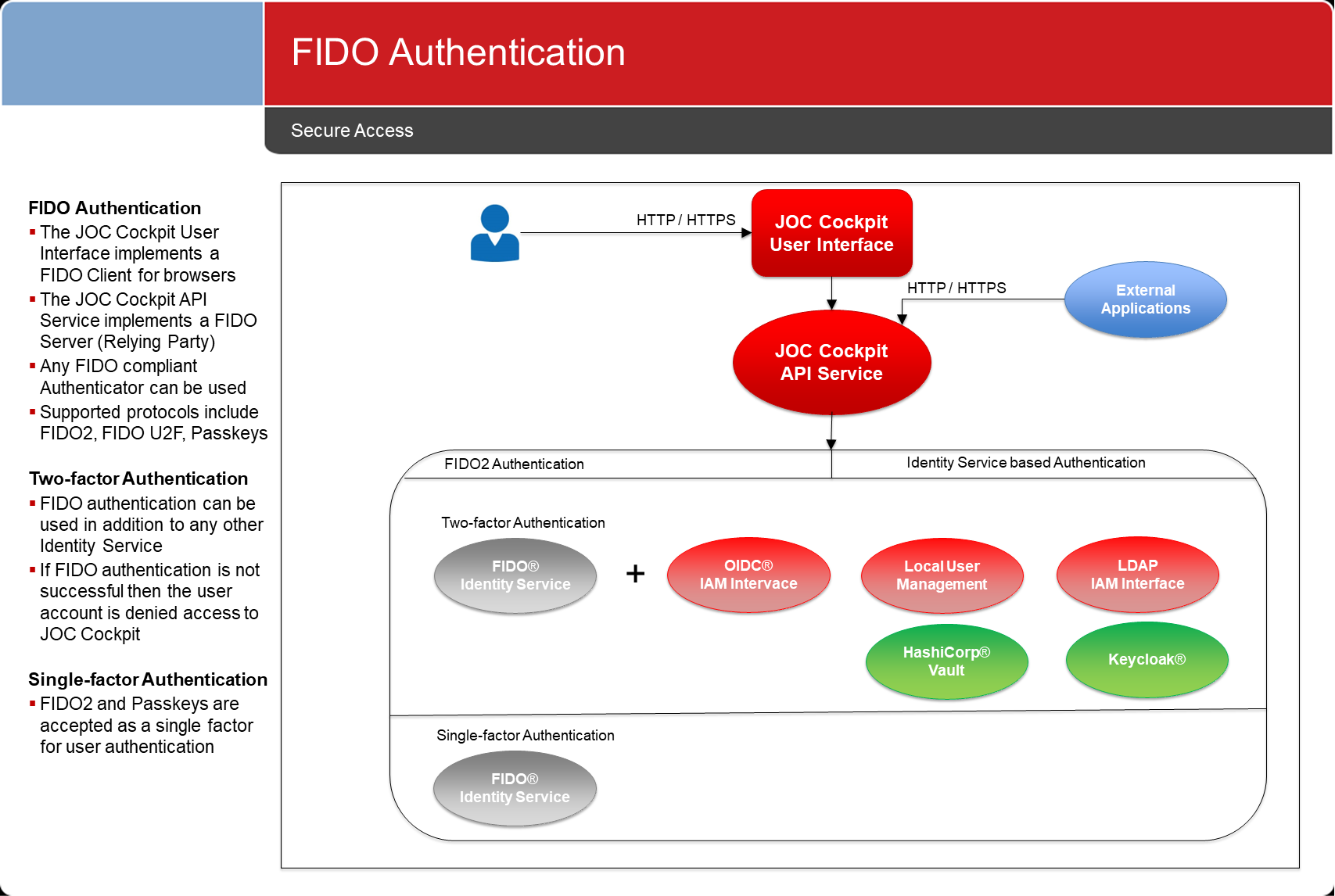
FIDO Authentication
The FIDO family of protocols offers FIDO2 and Passkeys as a single factor and as second factor in MFA. The FIDO U2F protocol can be used as a second factor.
For details see JS7 - FIDO Identity Service.
Credential Management
- Users frequently ask if JobScheduler can encrypt credentials. The answer is "no" as it makes no sense
...
- to handle a symmetric key
...
- that
...
- is stored in the JS7 configuration. Encrypting credentials contributes to obfuscation, not to security.
- There is only one way to handle passwords: not to use them.
- Alternatives include use of a JS7 - Credential Store.
References
- Find details in the JS7 - Secure Operation article.
Further Resources
...
- Microsoft SQL Server, see the How to connect to an SQL Server with a domain account article.
- Oracle that includes support for Oracle Wallet, see How to connect to an Oracle database without using passwords
Job Credentials
Default Configuration
- The Windows Service for the JobScheduler Master and Agent runs in the system account.
- The installer allows to specify a different account and to add credentials for that account.
- By default jobs are executed in the context of the account that the JobScheduler Master or JobScheduler Agent are operated for.
Secure Configuration
- It is a bad idea to run a JobScheduler Master or Agent using a Unix root account or Windows Administrator account.
- Certainly this makes life easy when it comes to switching to other user accounts or accessing files.
- However, you should not grant more permissions to a process than required.
- Use specific user accounts to run JobScheduler Masters and Agents:
- Do not use the system account (Windows) or root (Unix).
- Create specific service accounts that are limited to privileges that are required to execute jobs.
- Do not specify credentials for Windows Service accounts during installation:
- The installer will store such credentials in its installation response file (Master:
jobscheduler_install.xml, Agent:jobscheduler_agent_install.xml) - Instead, use the Windows Service Panel to manually specify credentials for the service account.
- The installer will store such credentials in its installation response file (Master:
- There are a number of options when it comes to running jobs for different user accounts:
- For Unix environments
- Your job scripts can switch to a different user context by use of
sudoorsucommands.sudois the preferred option as this the standard Unix tool that allows secure configuration of the users that are allowed to execute certain commands (sudoers file). In additionsudoprovides reporting capabilities about (ab)use of commands.
- Your job scripts can switch to a different user context by use of
- For Windows environments
- You can use the Windows Credential Manager to safely store credentials of the user account that a job should be executed for. The JobScheduler will then read the credentials and create a new process to run a job in the target user context. This is the preferred solution as it does not store credentials with the JobScheduler configuration.
- Find detailed information from the JobScheduler Universal Agent - Running jobs as a different user article.
- For all environments
- You can run a number of Agents in parallel for different user accounts.
- For details see the JobScheduler Universal Agent - Running multiple instances article.
- For Unix environments
- For jobs that require credentials, e.g. to access a database, a credential store can be used, see the Using a Credential Store for Jobs article.
- Credentials are not provided from parameters (that could be logged in clear text), instead an interface is provided that allows on demand access to the credential store.
- This feature is available for Shell jobs and for API jobs (JavaScript, PowerShell etc.).
File Transfer Credentials
Such credentials apply to use of the YADE file transfer utility that is available from built-in job templates.
Default Configuration
- By default any accounts/passwords that are used for source connections, target connections and proxy connections are stored in clear text.
- Find the YADE - Reference Documentation - Parameter Reference
Secure Configuration
...