FEATURE AVAILABILITY STARTING FROM RELEASE 1.9
Mode Of Operation
To use the SSH Session Management you have to configure your SSH Job and define a second jobchain for the cleanup work.
The feature is available only with the use of the JSch implementation by JCraft. To configure your SSH Job to use the JSch implementation, see How To - Usage of the SOSSSHJob2JSAdapter Job with JCrafts JSch .
The SSH Session Management checks and processes depending on the following conditions:
- remote process is running and the JobScheduler Task is still alive
- nothing to do, the cleanup jobchain goes to a setback condition and waits for another start
- remote process is running but the JobScheduler Task is not available anymore
- the cleanup job tries to end the process on the remote host
- remote process is not available anymore but the JobScheduler Task is still running
- the cleanup job ends the Task immediately
- remote process and the JobScheduler Task are not available anymore
- nothing to do, the cleanup job ends
Adjust the SSH Job to be monitored
To be able to monitor the SSH Job you have to add some additional parameters to the job configuration.
runWithWatchdog
- format:
- boolean
- default value:
false
- description:
- If this parameter is set to true, the job itself is aware that it is monitored and generates an new order for the second jobchain with all parameters of the job and the pid of the connected shell. If the parameter is set to false or is not present the SSH Session Management will not be processed.
cleanupJobchain
- format:
- String
- default value:
- empty
- description:
- This parameters defines the path to the configuration files of the jobchain to use for the cleanup work.
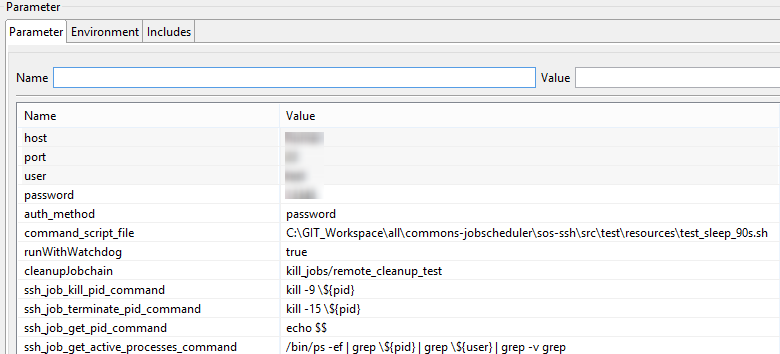
ssh_job_kill_pid_command
- format:
<command> \${pid}
- default value:
kill -9 \${pid}
- description:
- The command to kill a process on the remote machine. The command depends on the OS of the remote host. If the command is not set, the cleanup Job checks the remote host if it runs on Linux or Windows and uses the related default commands.
The placeholder${pid}will be substituted by the cleanup job and the leading $ character has to be escaped.
- The command to kill a process on the remote machine. The command depends on the OS of the remote host. If the command is not set, the cleanup Job checks the remote host if it runs on Linux or Windows and uses the related default commands.
ssh_job_terminate_pid_command
- format:
<command> \${pid}
- default value:
kill -15 \${pid}
- description:
- The command to terminate a process on the remote machine. The command depends on the OS of the remote host. If the command is not set, the cleanup Job checks the remote host if it runs on Linux or Windows and uses the related default commands.
The placeholder${pid}will be substituted by the cleanup job and the leading $ character has to be escaped with \.
- The command to terminate a process on the remote machine. The command depends on the OS of the remote host. If the command is not set, the cleanup Job checks the remote host if it runs on Linux or Windows and uses the related default commands.
ssh_job_get_pid_command
- format:
<command>
- default value:
echo $$
- description:
- A command or script to write the pid of the connected shell to stdout of the remote host.
ssh_job_get_active_processes_command
- format:
<command> \${pid} \${user}
- default value:
/bin/ps -ef | grep \${pid} | grep \${user} | grep -v grep
- description:
- The command or script to check if the process on the remote host is still running. The cleanup job expects an exitcode = 0 if the process is still running or other than 0 if the process is not available anymore. The command or script depends on the OS of the remote host. If the command is not set, the cleanup Job checks the remote host if it runs on Linux or Windows and uses the related default commands.
The placeholders${pid}and${user}will be substituted by the cleanup job and the leading $ character has to be escaped with \. - command example:
/bin/ps -ef- writes all running processes to stdout on the remote host
| grep \${pid}- filters the result to show only results containing the given ${pid}
- filters the result to show only results containing the given ${pid}
| grep \${user}- filters the result to show only results containing the given ${user}
| grep -v grep- filters the grep command itself
- filters the grep command itself
- The command or script to check if the process on the remote host is still running. The cleanup job expects an exitcode = 0 if the process is still running or other than 0 if the process is not available anymore. The command or script depends on the OS of the remote host. If the command is not set, the cleanup Job checks the remote host if it runs on Linux or Windows and uses the related default commands.
Example Configuration With JOE
Job:
Parameters:
Example XML Configuration
Configuration Of The Cleanup Jobchain
To process the cleanup of the remote processes or the JobScheduler task a second Jobchain with two jobs has to be configured.
The cleanup Jobchain consists of two Jobs, one to read the pid of the connected shell from a temporary file on the remote host and one to check if the process or the JobScheduler Task is still running and to end that remote process or the JobScheduler Task respectively.
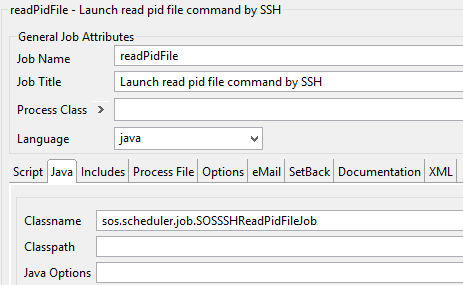
Job 1: The read-pid-from-temporary-file-Job
The first job reads the pid from a temporary file on the remote host. If your SSH Job is configured as described above, a temporary file is created on the remote host. Configure the Class of the Job in JOE like this:
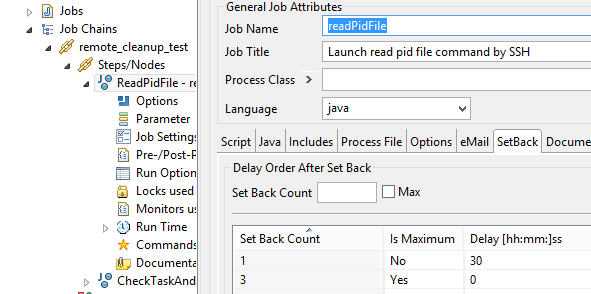
After choosing the relevant Classname from the list you have to configure a setback for the job. Depending on the checked condition as described above the setback will be used to restart the job.
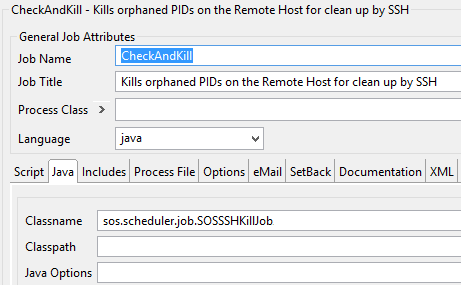
Job 2: The check-and-kill-Job
The second job checks if the pid determined by the first job is still active, if the JobScheduler Task is still active and kills the remote process or the JobScheduler Taskbased on the condition as desribed above. Configure the Class of the Job in JOE like this: