Page History
| Table of Contents |
|---|
Introduction
Amazon AWS® CloudWatch is a service of Amazon Web Services that monitors the customer's applications and resources running on the AWS® infrastructure in real time. It is used to track and to collect metrics, variables you can measure for your applications and resources. AWS® CloudWatch monitors resources like Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2®) instances, Elastic Load Balancing (ELB®), Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS®) volumes, and Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS®) instances.
JS7 can be integrated with the AWS® CloudWatch. This integration allows users to check the logs and current statistics in a graphical UI. Users can also detect and shut down unused or underused EC2® instances.
For JS7 JobScheduler as a Service, find the following suggested architecture.
Set up CloudWatch Agent
...
user interface.
Advantages of CloudWatch Logs
- CloudWatch Logs provides real-time application and System Monitoring.
- Long-term log retention.
- A view of the entire infrastructure.
- CloudWatch can be used to set alarms and to execute automatic actions.
- Users can tune their AWS services to deliver the highest performance and throughput using the metric data and logs.
User Benefits of CloudWatch Logs
- Easy to set up Alarms and Rules - In CloudWatch, users can set up Alarms to receive notifications while triggering the error messages from log files.
- Users can access all the data from a single dashboard. Lots of data can be accessed through a single CloudWatch Interface.
- CloudWatch Logs enables users to see all the logs as a single and consistent flow of events ordered by time. Users can query and sort them based on their dimensions, create custom computations with a powerful query language, group them by specific fields, and visualize log data in dashboards.
Setting up CloudWatch
Managing the IAM Role
Creating the IAM Role
IAM Role is an IAM identity that users create in their accounts for specific permissions. Basically, to access the AWS resources, the users require permissionpermissions. This role includes the permission policy that grants the permissions.
...
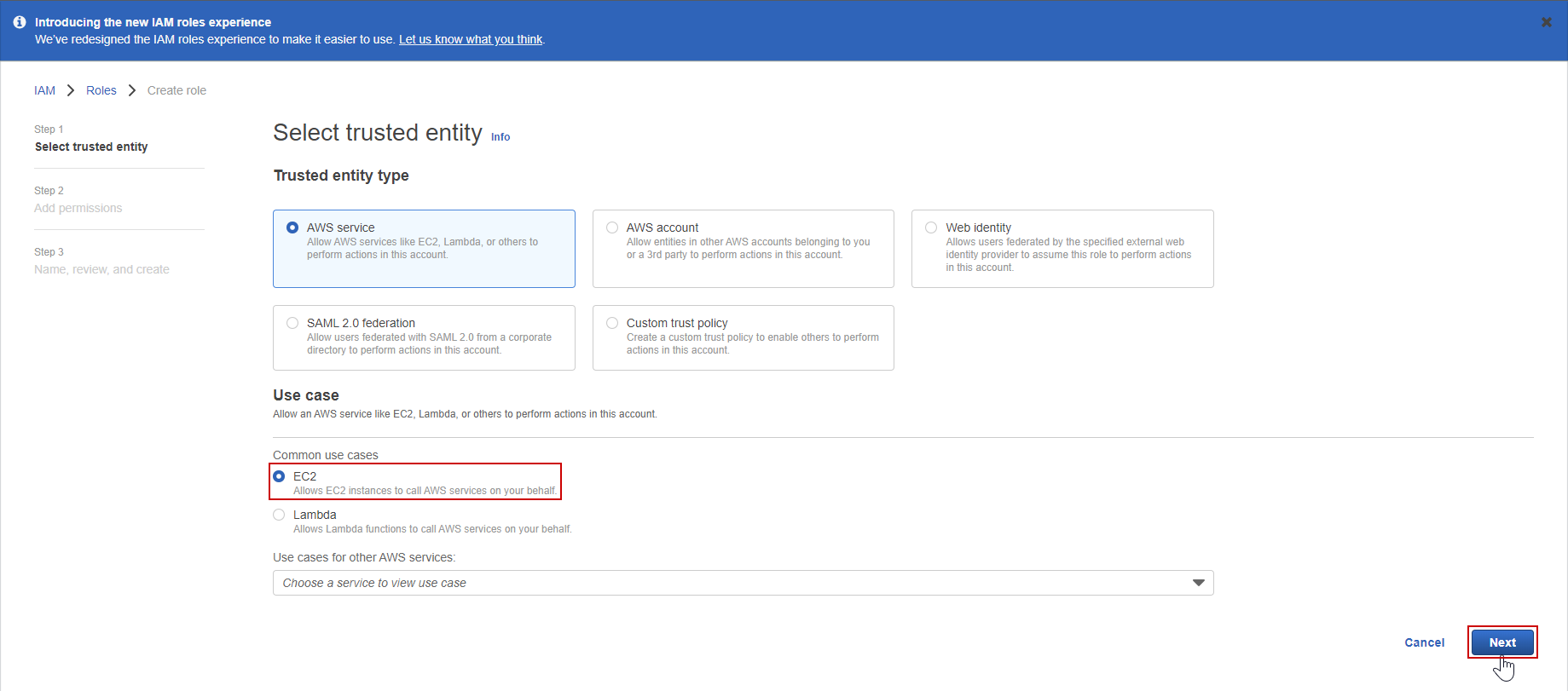
- Login to AWS® Management Console and open the IAM console. Select Roles from the menu and then click the Create role button.
- Select the service that will use this Role for the AWS® services (EC2, Lambda, and others). Select EC2 and click the Next: Permission button.
- To select your new role's policy , search for the CloudWatchAgentServerPolicy, check the checkbox and click the Next button.
- Provide the Role Name, Review review, and create the Role.
...
Attaching the IAM Role
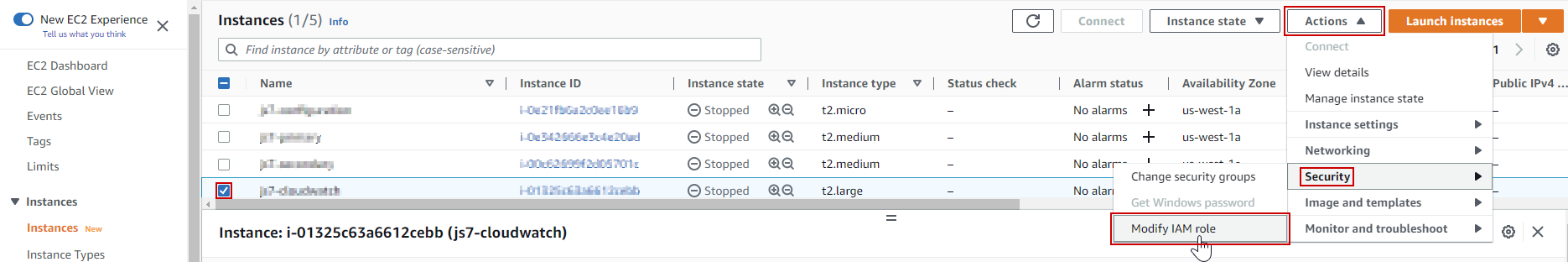
To allow an EC2 instance to connect with AWS® CloudWatch, the user must attach the IAM role to the EC2 Instance. It can be done through the AWS console or via the AWS Command Line Interface (CLI).
- Using the AWS Console
To attach the IAM Role, navigate to the EC2 Dashboard, select Instance from the menu and check the checkbox of the EC2 Instance. Click on the Actions dropdown and choose Security>Modify IAM Role.
Choose the newly created IAM Role and update the IAM Role. Using the AWS CLI
For AWS CLI Version 1.11.46, use the below command to attach the IAM Role:
| Code Block |
|---|
$ aws ec2 associate-iam-instance-profile --instance-id YourInstanceId<your-instance-id> --iam-instance-profile Name=CloudWatchAgentServerRole |
...
Installing the CloudWatch Agent
Run Users can run the following commands to connect to the EC2 instance. First, you need to install the CloudWatch Agent has to be installed from S3. Use the The below command can be used, for example to download it for AMD64 Ubuntu.
| Code Block |
|---|
$ wget https://s3.amazonaws.com/amazoncloudwatch-agent/ubuntu/amd64/latest/amazon-cloudwatch-agent.deb |
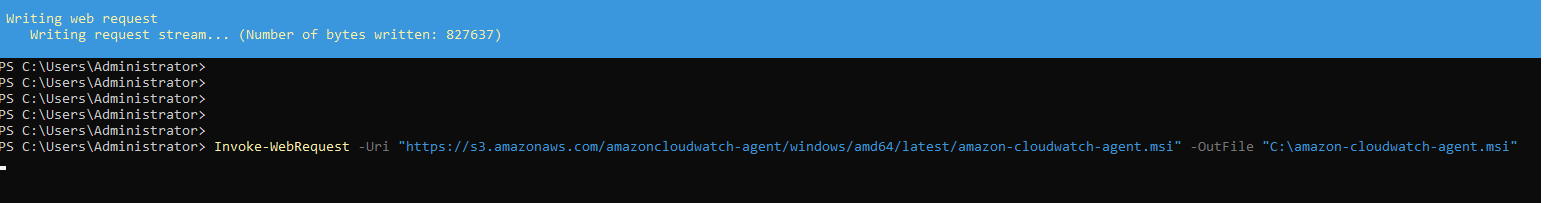
Use the The below command can be used to download it the CloudWatch Agent for Windows.
| Code Block |
|---|
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "https://s3.amazonaws.com/amazoncloudwatch-agent/windows/amd64/latest/amazon-cloudwatch-agent.msi" -OutFile "C:\amazon-cloudwatch-agent.msi" |
Use the following command to install the CloudWatch Agent on Ubuntu:
| Code Block |
|---|
$ sudo dpkg -i -E ./amazon-cloudwatch-agent.deb |
To install the CloudWatch Agent on Windows user need to execute , the below command from the path where the MSI installer file is installedexecuted:
| Code Block |
|---|
C:\> msiexec /i amazon-cloudwatch-agent.msi |
After installing the CloudWatch Agent, the user needs to be configured before it starts. It can be configured in two ways: by manually creating a config file or using the wizard (In which the user needs to answer a series of questions). It that generates a config configuration file.
...
Manually
...
Creating config.json
The log agent uses the config file. Users need to create it at the below path:CloudWatch Agent makes use of a configuration file that, by default, is looked up from the below path:
If this file is unavailable from the below path, the user must create it manually.
| Code Block |
|---|
/opt/aws/amazon-cloudwatch-agent/bin/config.json |
From the above path, users can create or edit the config configuration file with the following content:
| Code Block |
|---|
{
"agent": {
"run_as_user": "root"
},
"logs": {
"logs_collected": {
"files": {
"collect_list": [
{
"file_path": "{path to your log file}",
"log_group_name": "scheduler-error-log",
"log_stream_name": "{instance_id}"
}
]
}
}
}
} |
In the above config example the file, "file_path" is specifies the path to the log file from which the user wants to collect data from e.g., controllerdata should be collected, for example /var/sos-berlin.com/js7/controller/ontroller.log, agent.log. For the naming of Log Group and Log Streams, The log_group_name and log_stream_name settings can be used respectively in the to specify the names of Log Group and Log Stream in CloudWatch.
...
Running the Wizard
Follow Execute the below command to start the wizard run for Ubuntu:
| Code Block |
|---|
$ sudo /opt/aws/amazon-cloudwatch-agent/bin/amazon-cloudwatch-agent-config-wizard |
Follow Execute the below command to start the wizard run for Windows:
| Code Block |
|---|
C:\> cd "C:\Program Files\Amazon\AmazonCloudWatchAgent"
.\amazon-cloudwatch-agent-config-wizard.exe |
In the wizard run, the config.json file is automatically created. Before the creation of The wizard automatically creates the config.json file , it having asked for a number of questions as the Log Agent used to collect related to collecting system-level metrics, so users need to answer these questions and can ignore the questions that are not related to collecting logs. While . When using the wizard, users can always take use the generated config configuration file and then manually add it to any additional EC2 instances.
Start the Agent
Starting the CloudWatch Agent
Users can run Run the below command to execute the CloudWatch Agent on Ubuntu Server.:
| Code Block |
|---|
$ sudo /opt/aws/amazon-cloudwatch-agent/bin/amazon-cloudwatch-agent-ctl -a fetch-config -m ec2 -c file:/opt/aws/amazon-cloudwatch-agent/bin/config.json -s |
Run Users can run the below command to execute the CloudWatch Agent on Windows Server.:
| Code Block |
|---|
PS C:\> & "C:\Program Files\Amazon\AmazonCloudWatchAgent\amazon-cloudwatch-agent-ctl.ps1" -a fetch-config -m ec2 -s -c file:config.json |
...
Viewing Logs
From In the CloudWatch Overview, the user users can select Logs from the menu. The user can Users find the label for the Log Group created in the configuration of Logs. Select Selecting the Log Group name Name allows to see the Log Streams. Click on Clicking the Log Stream uses specifies the EC2 instance ID, so the user knows in which EC2 instance the from which data is logged.
The user needs to search in CloudWatch Logs provides good search capabilities. Users can use the filter text box to filter the required logs. All the searched logs will appearsearch in logs. Also, it can create alerts or notify users when triggering error messages or warnings from log files.