Page History
...
Workflow Name: A workflow is assigned to which an order is added per incoming file.Agent: An Agent is assigned that performs file watching. Standalone Agents and Agent Clusters can be assigned. In an Agent Cluster the active Director Agent performs file watching, Subagents do not perform file watching.Directory: The directory that the Agent watches for incoming files:- Unix: A path can be specified such as
/tmp/incoming - Windows: A path can be specified with backslashes or forward slashes such as
C:\tmp\incomingandC:/tmp/incoming - Unix, Windows: OS environment variables can be used that are known to the Agent, for example from its Instance Start Script. Environment variables and constant strings can be concatenated using the
++operator and considering quoting for constant strings like this:- Unix:
env("HOME") ++ '/incoming' - Windows:
env("TMP") ++ '/incoming'
- Unix:
- Unix: A path can be specified such as
Pattern: The pattern to match an incoming file is not a wildcard expression such as *.csv, instead it represents a Java Regular Expression. The pattern has to match the path of an incoming file including the directory hierarchy, not just the file name. Consider the following examples:- match any files:
.* - match files with a .csv extension:
.*\.csv$ - match files that end with a date in yyyy-mm-dd format:
.*\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2}$
- match any files:
Delay: The delay in seconds for which a file is checked to be stable and does not change its size or timestamp.
Using Files in Workflows
Using File Paths
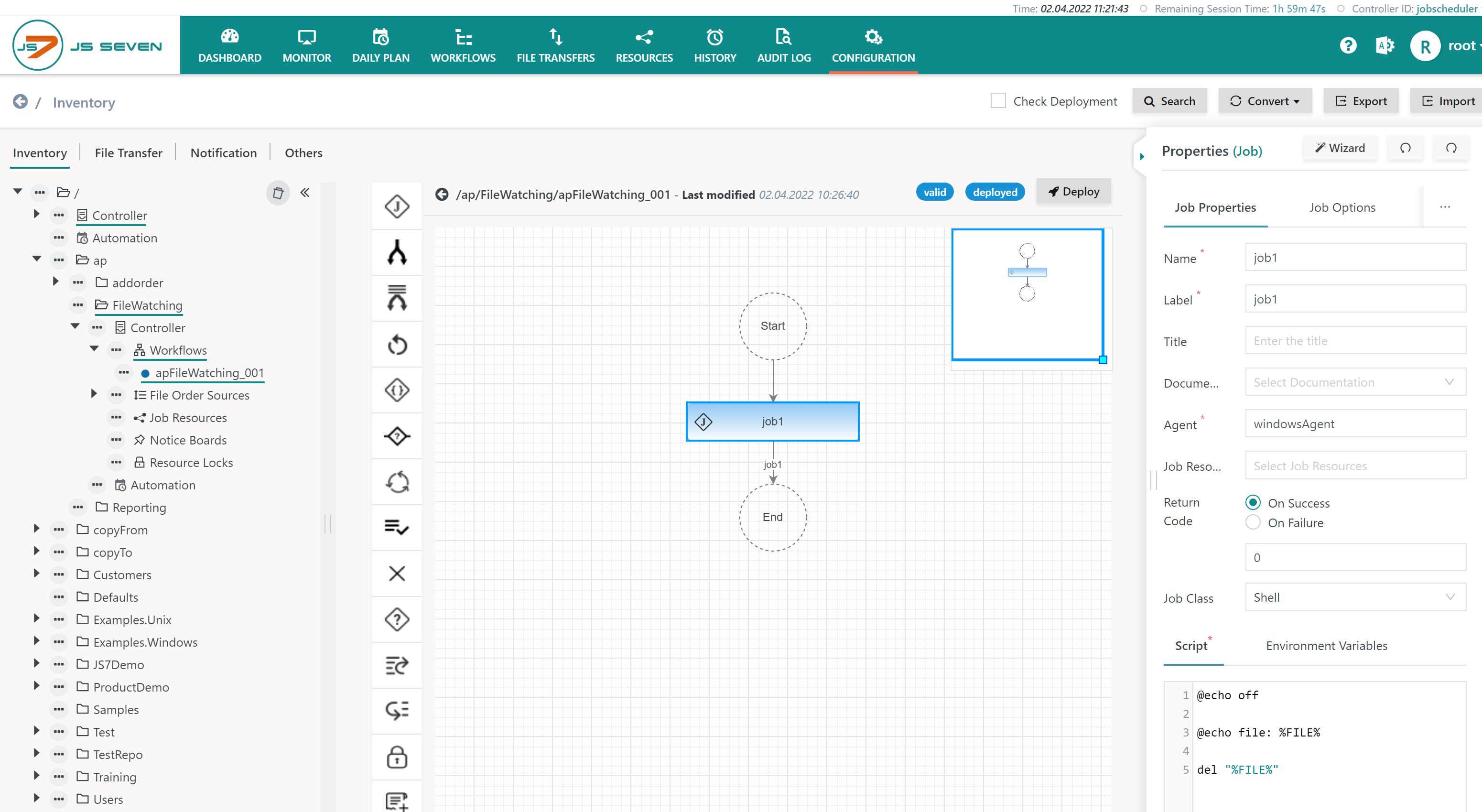
For incoming files the JS7 File Order Source provides a built-in variable $file that holds the path to the incoming file. This variable does not have to be declared but can be used for example to create an environment variable that is used from a job script:
...
- The below example shows a Windows job script using
%FILE%. - For Unix an environment variable is used from
$FILEor${FILE}.
Using File Names
The built-in $file variable holds the full path of the incoming file, for example /tmp/incoming/test.txt.
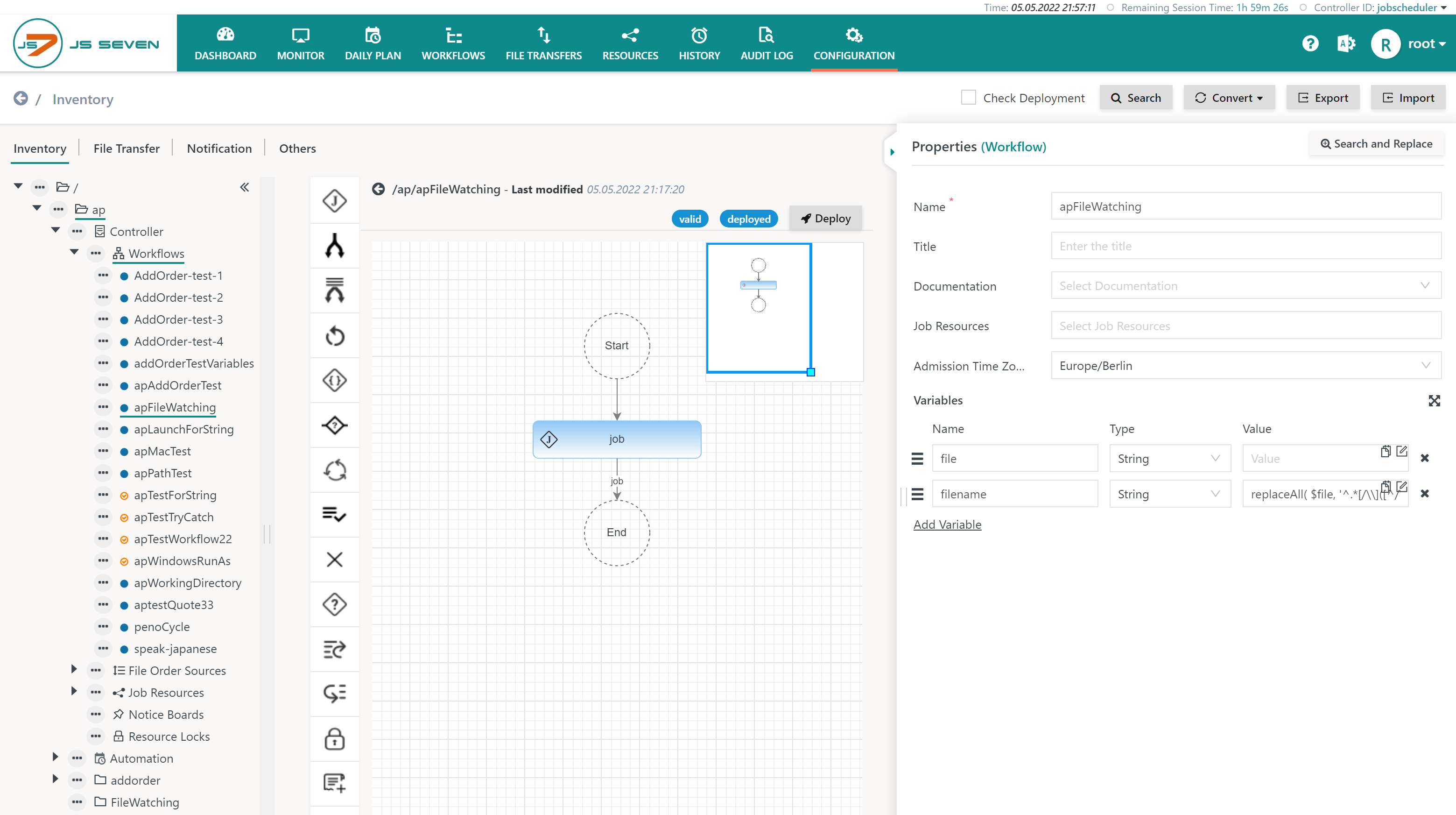
Users who want to use a file name such as test.txt instead of the full path can configure their workflow like this:
Explanation:
- Two workflow variables are declared:
- The built-in
$filevariable is declared without a default value. - A new
$filenamevariable is declared (an arbitrary name can be chosen for the variable).- The assigned value is a generic expression that extracts the file name from the incoming file's full path:
replaceAll( $file, '^.*[/\\]([^/\\]+)$', '$1' )
- The built-in
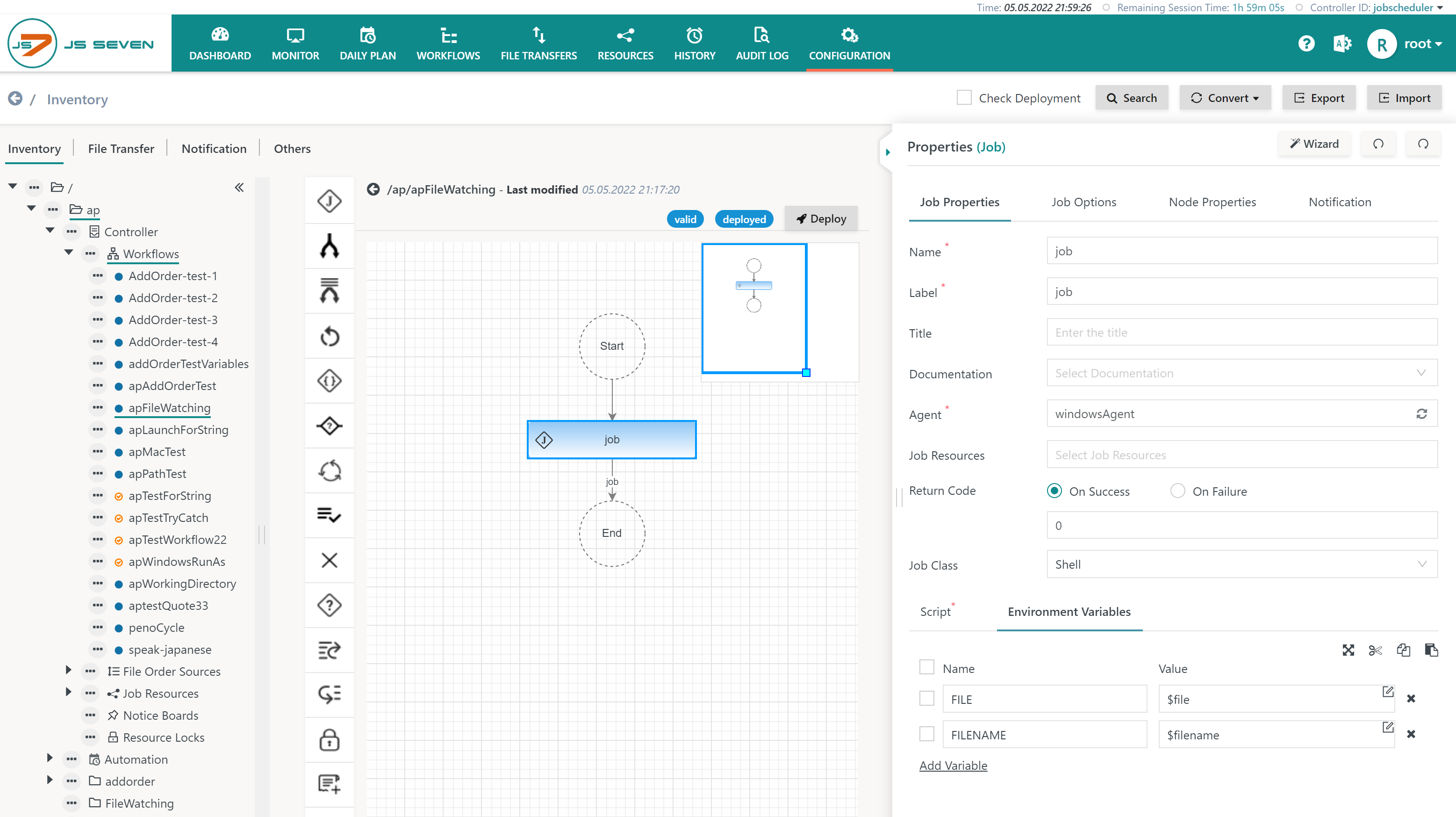
- The assignment of environment variables for a job can make use of both declared variables.
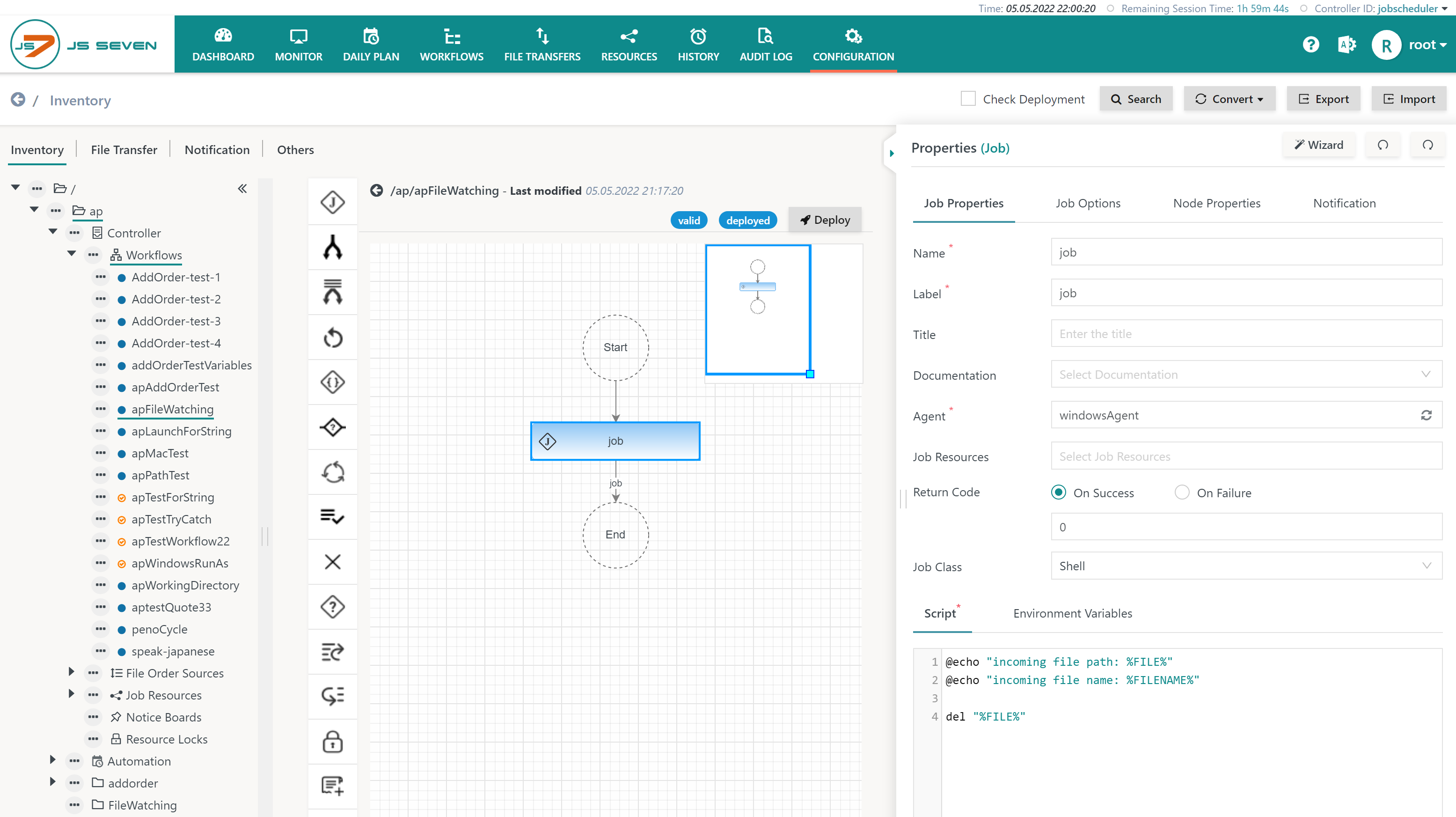
In the job script the environment variables FILE and FILENAME can be used like this:
- The below example shows a Windows job script using
%FILE%and%FILENAME%. - For Unix environment variables are used from
$FILEor${FILE}and$FILENAMEor${FILENAME}.
File Handling
Checking for Incoming Files
...
Overview
Content Tools